Figure 4.
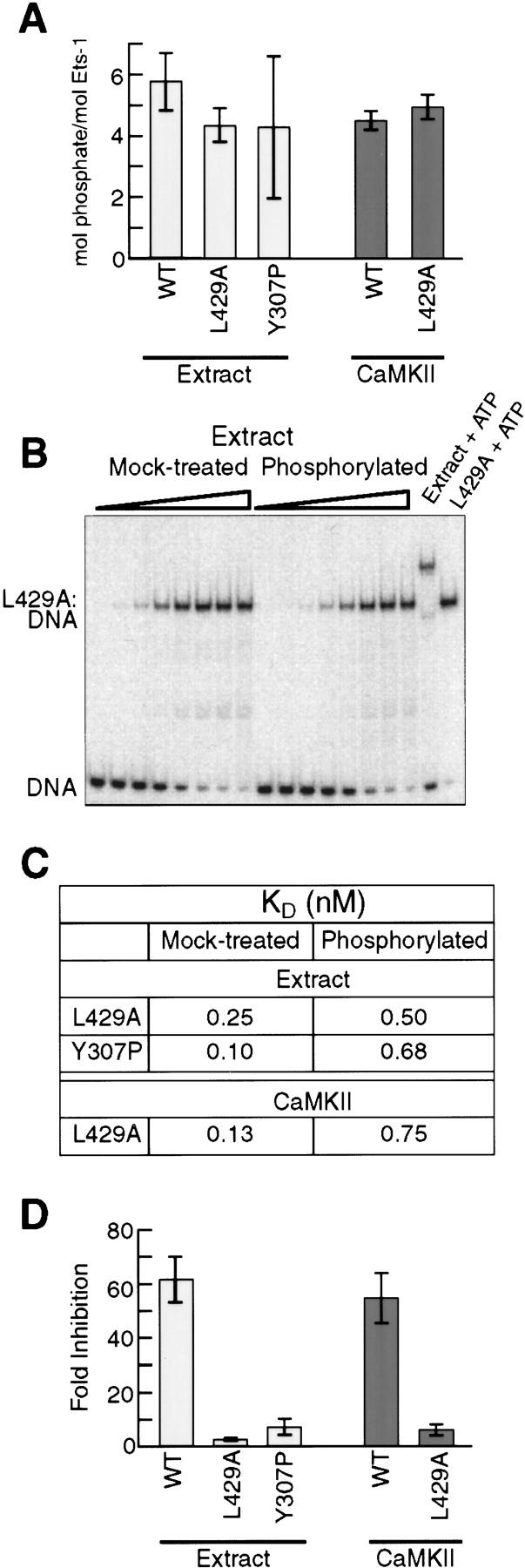
A disrupted inhibitory module impairs phosphorylation-dependent repression of DNA binding. (A) Phosphorylation of wild-type Ets-1 and inhibitory-module mutants by nuclear extract or CaMKII. Bars indicate mean phosphate incorporation (±s.d.) from three experiments. (B) Equilibrium DNA-binding studies of L429A. L429A was treated with nuclear extract without (mock-treated) or with (phosphorylated) ATP. Reaction mixtures were diluted into DNA-binding buffer and analyzed by EMSA. (C) Kd of mock-treated and phosphorylated L429A and Y307P. L429A and Flag–Y307P were treated with nuclear extract and analyzed as in B; L429A was treated with CaMKII and analyzed as in Fig. 2D. Kd values were obtained from mean data points of three experiments. (D) Phosphorylation-dependent inhibition of wild-type Ets-1, L429A, and Y307P. Mean (±s.d.) inhibition values were determined from Kd values of two [extract-treated wild-type (WT)] or three (all others) individual EMSA experiments. Extract-treated wild-type represents inhibition of Flag–Ets-1 repurified from nuclear extract as in Fig. 2C.
