Figure 2.
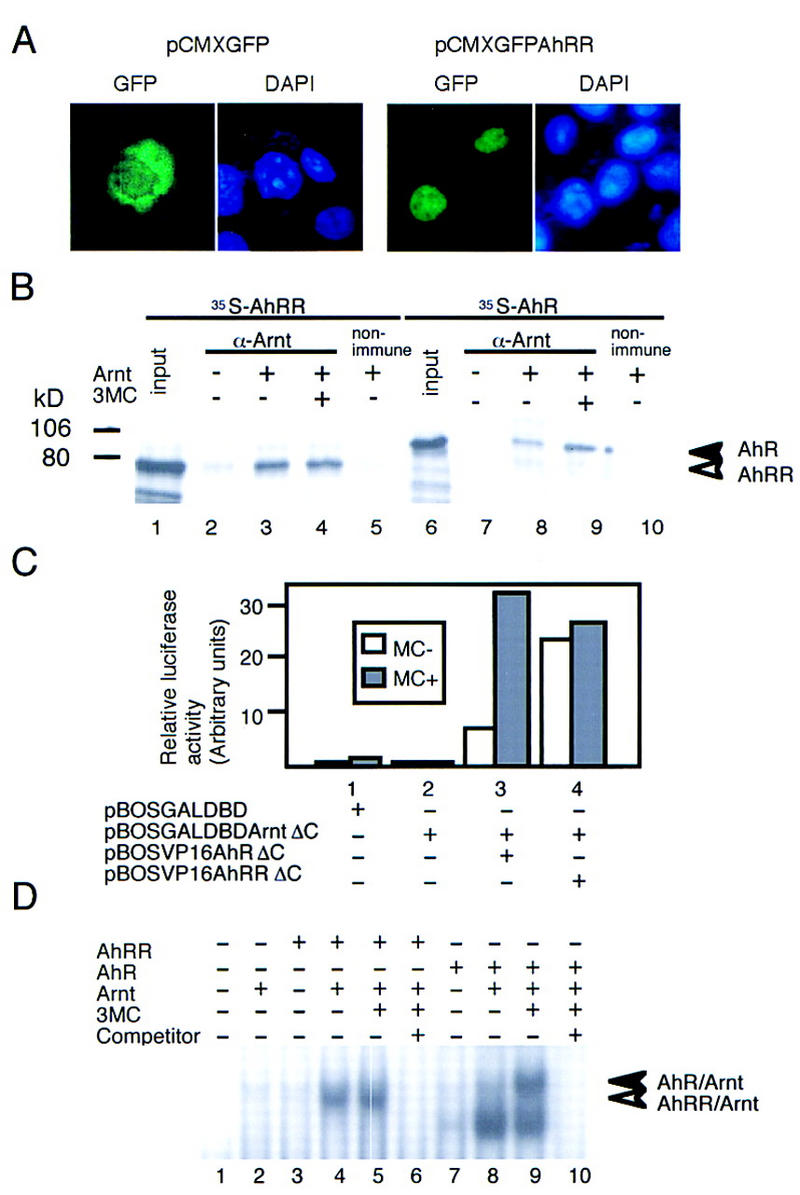
Subcellular localization of AhRR, heterodimer formation of AhRR with Arnt, and its binding to XRE sequence. (A) Subcellular localization of GFP–AhRR fusion protein. To construct pCMX–GFP–AhRR, an EcoRI–SalI fragment of AhRR was ligated with the SalI–BamHI site of pCMX–GFP–hGR (Ogawa et al. 1995). GFP (left) or GFP–AhRR fusion protein (right) was expressed in COS7 cells and visualized as described (Ogawa et al. 1995). (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of AhRR and AhR with an anti-Arnt antibody in the presence or absence of 3MC. Open and closed arrowheads indicate coprecipitated AhRR and AhR, respectively. (C) Interaction between AhRR or AhR and Arnt revealed by the mammalian two-hybrid method. A fusion gene encoding GAL4–DBD and Arnt–bHLH–PAS as bait and those encoding AhR or AhRR bHLH–PAS and VP16 AD were constructed. Various prey/bait combinations were cotransfected into 293 cells with pG3E–Luc; interaction of AhR or AhRR with Arnt was assessed by measuring the expressed luciferase activity. 3MC (1 μm) was used as inducer. (D) In vitro interaction of AhRR/Arnt heterodimer with XRE sequence. (Lanes 6,10) Nonlabeled XRE (250-fold) was used as competitor. Open and closed arrowheads indicate AhRR–Arnt–XRE and AhR–Arnt–XRE complexes, respectively.
