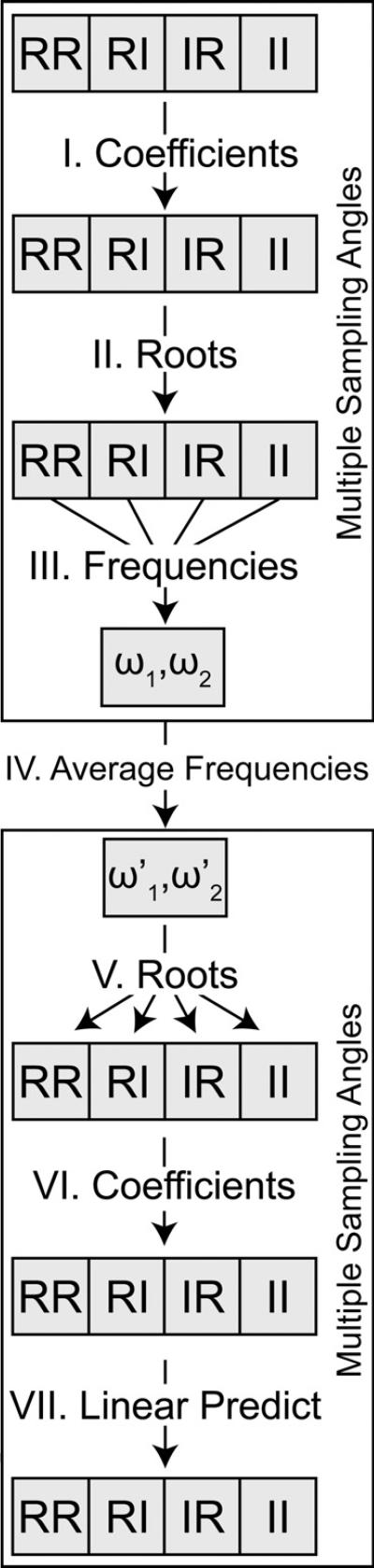
Fig. 1.
A general overview of the average linear prediction algorithm. The algorithm works by calculating a set of linear prediction coefficients in parallel for each radial sampling angle data set quadrature component. The coefficients are then used to solve for the characteristic polynomial roots, which in turn are combined to estimate the underlying amplitude and frequency components. The frequency components are averaged across all angle data sets. Finally, an improved set of coefficients are back-calculated. The improved set of coefficients can be used to predict additional data points with improved accuracy.