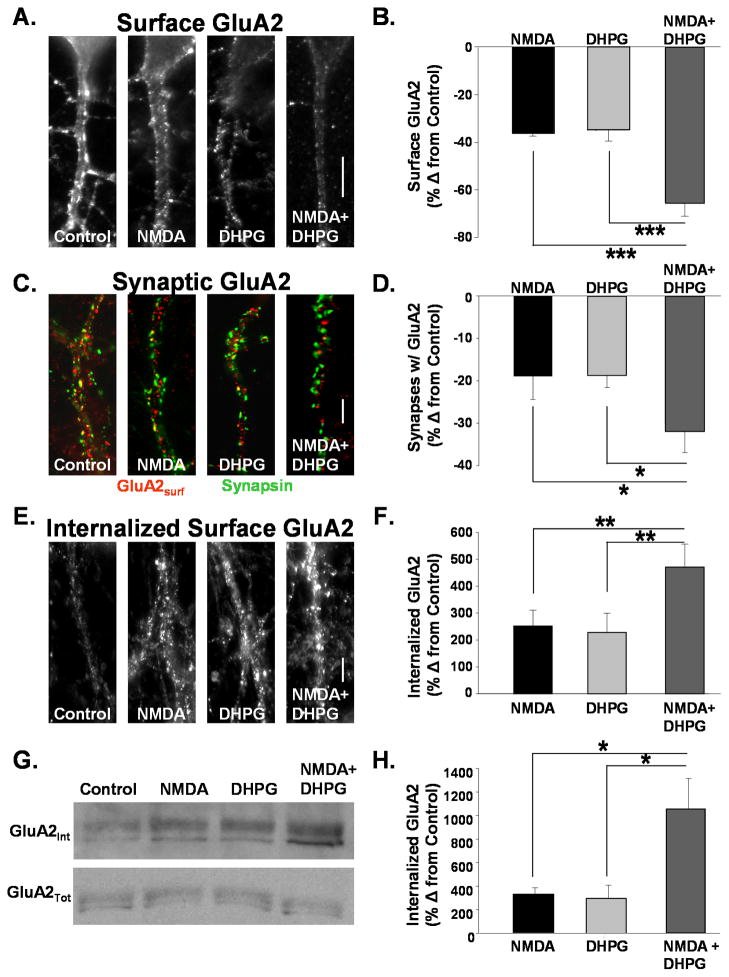
Figure 1. AMPAR internalization mediated by NMDAR and mGluR activation is additive.
A. Images depict surface GluA2 receptors on dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons treated with ACSF (control), NMDA (50uM, 2 min), DHPG (20 μM, 3 min), or both agonists together. Surface GluA2s were labeled in live neurons prior to treatment. Fifteen minutes after agonist addition cells were fixed and immunolabeled for remaining surface-expressed receptors. (Scale bar = 5μm) B. Quantitation of surface GluA2 AMPAR immunofluorescence from cells in experiments described in A. Activation of both pathways resulted in a nearly additive loss of surface AMPARs. (n=16, *** P<0.001). C. Images depict the expression of surface GluA2s and synapsin on dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons treated with ACSF (control), NMDA (50uM, 2 min), DHPG (20 μM, 3 min), or both agonists together. DHPG and NMDA application together caused a much greater reduction in synapsin puncta colocalized with GluA2 than did either agonist alone (Scale bar = 5μm) D. Quantitation of surface GluA2 AMPAR immunofluorescence from cells in experiments described in C. Activation of both pathways resulted in a nearly additive loss of surface AMPARs (n=5, * P<0.05). E. Images depict internalized GluA2s in dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons treated with ACSF (Control) NMDA (50uM, 2 min), DHPG (20 μM, 3 min), or both agonists together. Surface GluA2s were labeled in live neurons prior to agonist addition. Following treatments antibodies bound to GluA2s remaining at the membrane surface were stripped with an acidic solution. Cells were then fixed and immunolabeled for antibody bound receptors internalized from the surface with agonist stimulation. (Scale bar = 5μm) F. Quantitation of internalized surface GluA2 AMPAR immunofluorescence from cells in experiments described in E. Activation of both pathways resulted in a nearly additive increase of internalized surface AMPARs (n= 5, ** P<0.01). G. Western blots were probed for GluA2 to detect internalized surface (top) and total (bottom) GluA2 after agonist stimulation in hippocampal acute slices. Surface proteins were labeled with cleavable biotin prior to agonist treatment. After biotin was cleaved from remaining surface proteins, lysates were subjected to avidin precipitation to isolate internalized protein. H. Quantitation of blots in G. The increase in internalized GluA2 labeling intensity is plotted as a percent change from control. Activation of both NMDAR and mGluR pathways resulted in a slightly greater than additive increase in internalized GluA2 (n=4, * P<0.05).