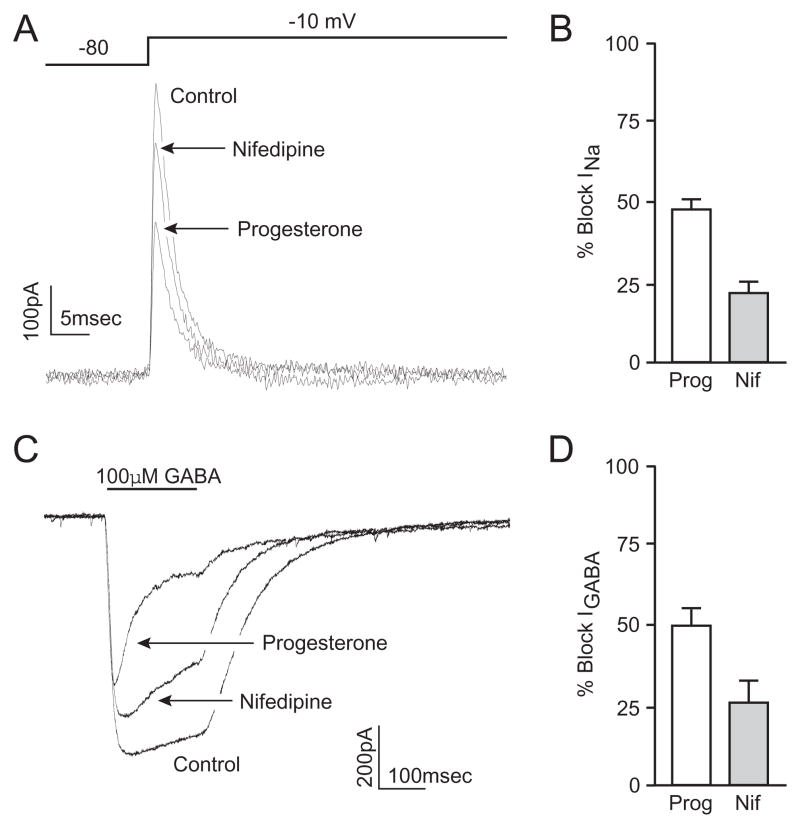
Figure 2.
Progesterone inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels and GABAA-mediated whole-cell currents. (A) Representative traces of whole cell sodium currents evoked by a voltage step from −80 to 0 mV under control conditions, and in the presence of progesterone or nifedipine. (B) Bar graphs summarizing the inhibition of sodium current by progesterone (47 ± 4%) and nifedipine (20 ± 4%) (C) Representative traces of whole-cell voltage clamp recordings during a 200 ms application of GABA (100 μM) under control conditions, and in the presence of progesterone or nifedipine. (D) Bar graphs summarizing the inhibition of GABAA-mediated peak current by progesterone (49 ± 6%) and nifedipine (25 ± 7%).