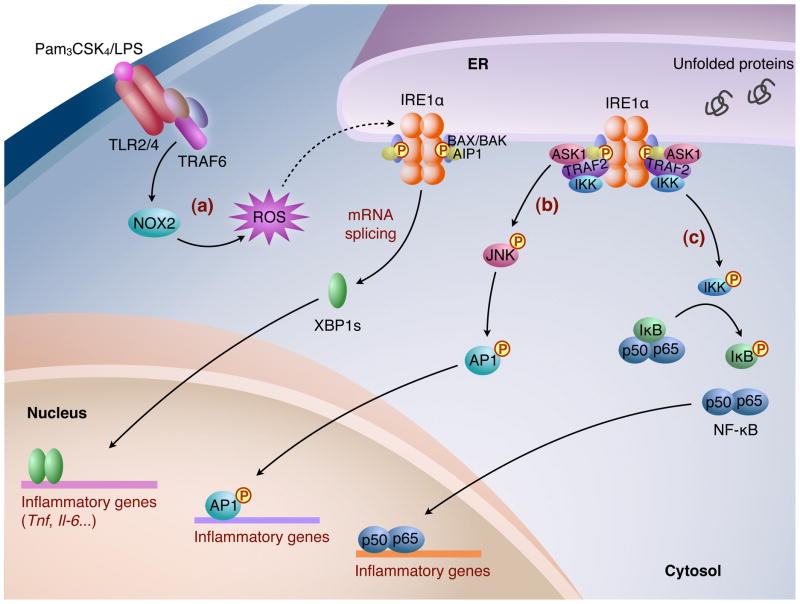
Figure 2.
The IRE1α-XBP1 pathway in inflammation. (a) In macrophages, upon ligand activation, TLR2/TLR4 recruits adaptor proteins including TRAF6 and induces NOX2-dependent production of ROS, which leads to IRE1α activation. Subsequently, XBP1s induces transcription of inflammatory cytokines, such as Tnf and Il-6. The recruitment of adapter proteins to IRE1α, such as BAX/BAK and AIP1, seems to be important for optimal activation of IRE1α, and for Xbp1 mRNA splicing and JNK activation. (b) In response to ER stress, the cytoplasmic domain of IRE1α forms a complex containing TRAF2 and triggers the activation of ASK1/JNK, which subsequently phosphorylates AP1. (c) The IRE1α-TRAF2 complex interacts with and activates IKK, which IKK initiates the degradation of IκB by phosphorylation, leading to nuclear entry of NF-κB. Activated AP1 and NF-κB then induce the transcription of genes involved in inflammation.