Figure 5.
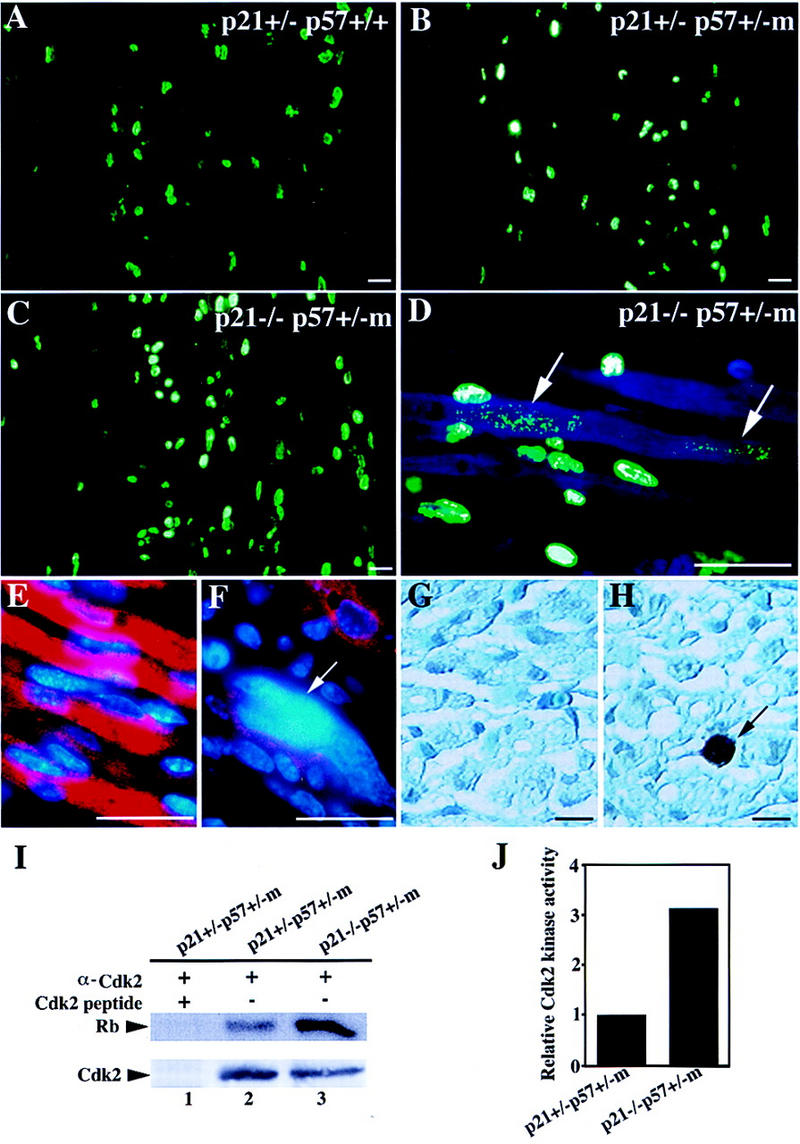
Increased rates of proliferation and apoptosis in p21/p57 double mutants. (A–D) BrdU pulse-labeled cells in the intercostal region of E16.5 embryos were visualized by immunofluorescence staining with a monoclonal antibody against BrdU that was subsequently detected with a FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. Arrows indicate BrdU-positive nuclei in the residual myotubes that were revealed by background DAPI (blue) staining. (E,F) MHC immunofluorescence staining of transverse sections of the abdomen region of E18.5 p21+/− p57+/+ (E) and p21−/− p57+/−m (F) embryos as in Fig. 4. Nuclei are visualized with DAPI staining (blue). Arrow indicates a giant nucleus. (G,H) TUNEL assays performed on transverse sections of the chest region of E16.5 p21+/− p57+/+ (G) and p21−/− p57+/−m (H) embryos. Arrow indicates an apoptotic nucleus in the intercostal muscle. (I) The activity of CDK2 kinse immunoprecipitated from muscle extracts was assayed using Rb as a substrate by measuring the incorporation of [γ-32P]ATP (top). The amount of CDK2 protein present in the immunoprecipitates monitored by Western blotting (bottom). (Lane 1) Immunoprecipitation from p21+/− p57+/−m muscle extracts using anti-CDK2 antibody neutralized with excess competing peptide; (lane 2) immunoprecipitation from p21+/− p57+/−m muscle extracts; (lane 3) immunopricipitation from p21−/− p57+/−m muscle extracts. (J) Quantitation of assays in I by PhosphorImager. Scale bars, 200 μm.
