Figure 2.
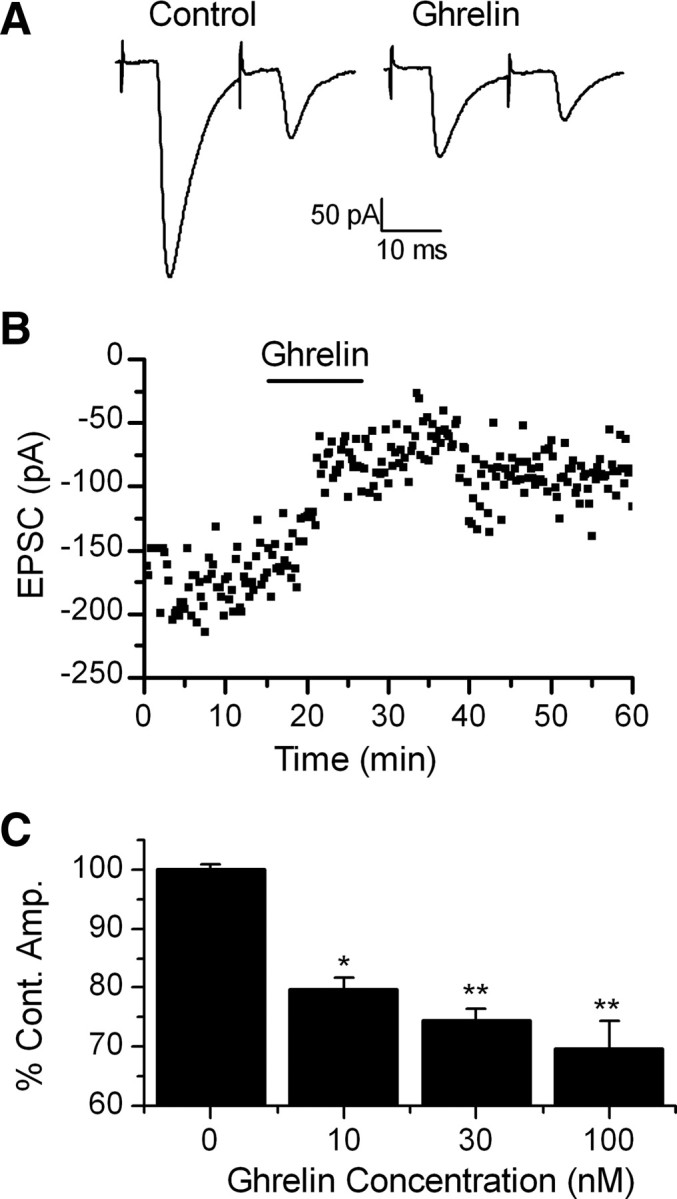
Ghrelin inhibits the amplitude of ST-stimulated EPSCs in TH-EGFP neurons. A, Representative trace of two ST-stimulated EPSCs. ST activation evoked monosynaptic EPSCs in TH-EGFP neurons. VM, −60 mV. Ghrelin significantly inhibited the amplitude of the ST stimulated EPSCs. This effect was partially reversed after a 10 min wash. B, A graph showing the effect of ghrelin on ST-EPCS amplitude over time in a representative neuron. C, Dose–response relationship showing the average change in ST-EPSC amplitude compared with a 10 min control exposure to ACSF (0 nm) with increasing doses of ghrelin. The results are not cumulative but reflect the result after a single 10 min exposure of the TH-EGFP neuron to only one dose of ghrelin. n = 7–11 for each dose. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus control (ACSF), one-way ANOVA. Error bars indicate SEM.
