Figure 5.
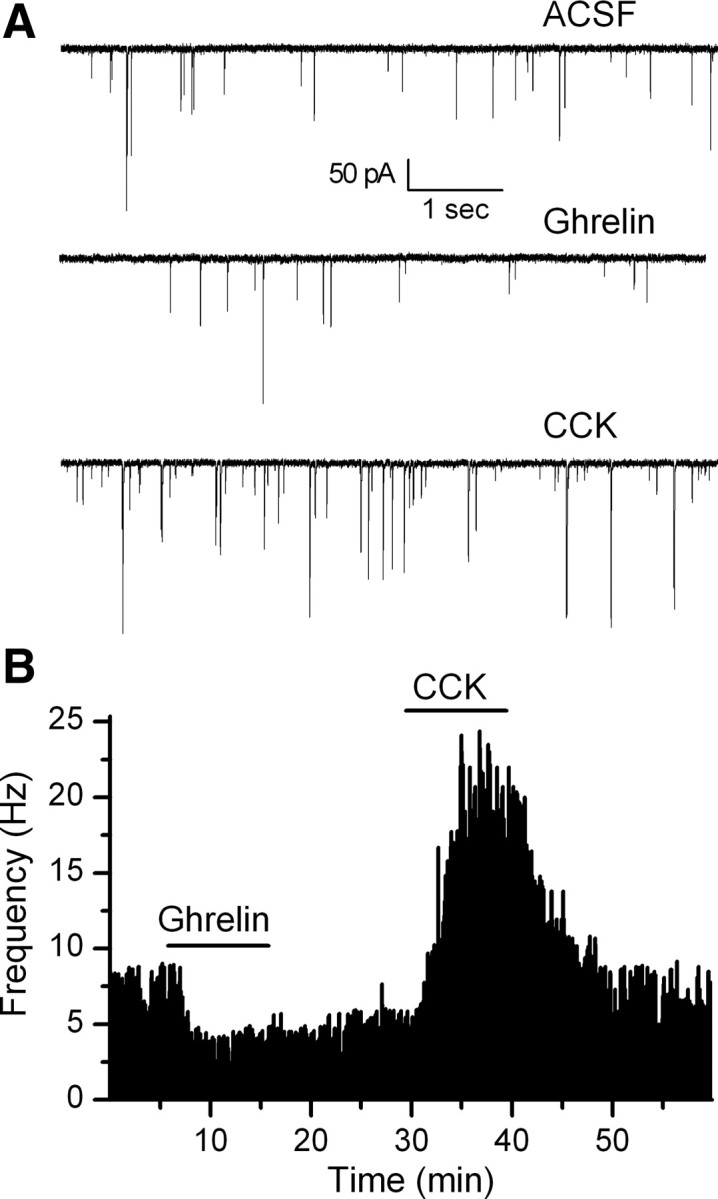
Ghrelin inhibits sEPSC frequency in CCK-sensitive and insensitive TH-EGFP neurons. A, Representative traces from control conditions (ACSF), after a bath application of ghrelin (100 nm) and a subsequent application of CCK (100 nm) in the same neuron. B, Graph showing the change in sEPSC frequency over time. This representative neuron responded first to ghrelin and then to CCK. Ghrelin had a significant effect in four of six CCK-sensitive and three of five CCK-insensitive neurons tested.
