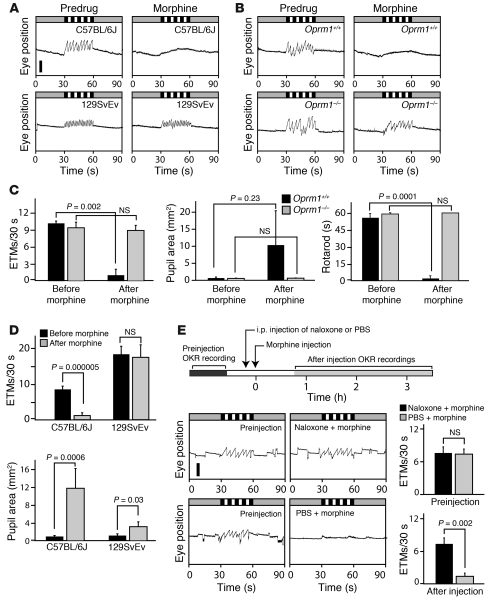
Figure 7. Strain differences, receptor specificity, and agonist-antagonist interactions analyzed by eye-movement analysis.
(A) Morphine (200 mg/kg, oral delivery) eliminates the OKR in C57BL/6J mice but not in 129SvEv mice. Scale bar: 0.5 mm. (B) OKR suppression by 200 mg/kg morphine is eliminated in Oprm1–/– mice but not Oprm1+/+ littermates in a C57BL/6J background. (C) Quantification of the effects of 200 mg/kg morphine on the OKR, pupil dilation, and rotarod performance in Oprm1–/– and Oprm1+/+ littermates. (D) Quantification of OKR suppression and pupil dilation in C57BL/6J and 129SvEv mice in response to 200 mg/kg morphine. (E) Naloxone blockade of morphine-induced suppression of the OKR. Time line of drug administration and OKR recordings (top). Representative OKR traces (bottom left). Quantification of ETM30 (bottom right). i.p. naloxone administered at 10 mg/kg 10 minutes before 200 mg/kg oral morphine blocked morphine-induced OKR suppression. Data in C and E are averages from 3 Oprm1–/– and Oprm1+/+ mice. Data in D are averages from 6 C57BL/6J and 4 129SvEv mice. Scale bar: 1 mm. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.