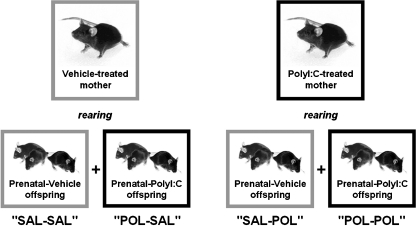
Fig. 1.
Experimental design for the postnatal cross-fostering procedure. Pregnant mice on gestation day 17 were exposed to PolyI:C (POL; 5 mg/kg, i.v.) or saline (SAL) solution. On the day of birth, offspring born to PolyI:C- and saline-treated dams were simultaneously cross-fostered to surrogate rearing mothers, which had either experienced inflammatory (PolyI:C) or sham (saline) treatment during pregnancy. This cross-fostering procedure resulted in four experimental treatment groups: (1) offspring subjected to prenatal saline exposure and raised by a saline-treated surrogate mother (SAL-SAL), (2) offspring subjected to prenatal saline exposure and raised by a PolyI:C-treated surrogate mother (SAL-POL), (3) offspring subjected to prenatal PolyI:C exposure and raised by a saline-treated surrogate mother (POL-SAL), and (4) offspring subjected to prenatal PolyI:C exposure and raised by a PolyI:C-treated surrogate mother (POL-POL)