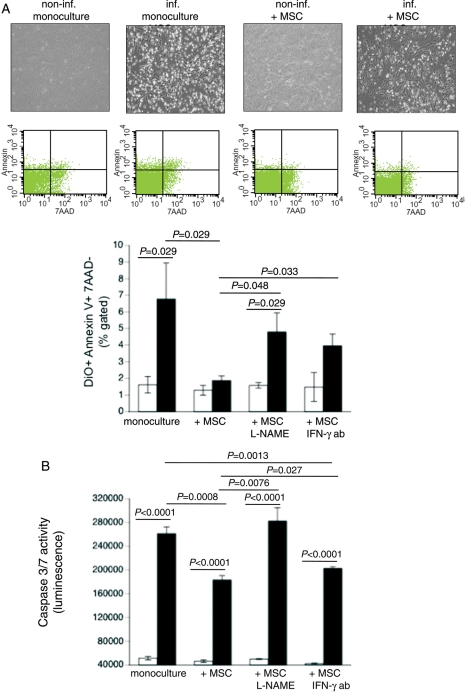
Figure 2.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) reduce coxsackievirus B3-induced apoptosis in a nitric oxide-dependent way and require priming via interferon-γ (IFN-γ). DiO-labelled HL-1 cells were cultured in a six-well plate and 24 h later infected with coxsackievirus B3 under serum-starvation conditions at a m.o.i. of 5. Four hours later, MSCs were added at a ratio of 1 to 10 HL-1 cells. After 24 h, cells were collected for annexin V/7AAD FACS analysis. (A) Upper panel shows representative pictures of non-infected HL-1, non-infected HL-1 co-cultured with MSCs, infected HL-1, and infected HL-1 co-cultured with MSCs; middle panel demonstrates representative pictures of annexin V/7AAD dot plots on pre-selected DiO+ HL-1 cells. Lower panel: bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM of DiO+ annexin V+/7AAD- HL-1 cells in cultures of HL-1 with or without untreated or L-NAME-treated MSCs or MSCs in the presence or absence of 1 µg/mL of IFN-γ antibody (ab); n= 4/group. (B) Bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM of caspase 3/7 activity in cultures of HL-1 with or without untreated or L-NAME-treated MSCs or MSCs in the presence or absence of 1 µg/mL of IFN-γ antibody (ab); n= 6/group.