Figure 1.
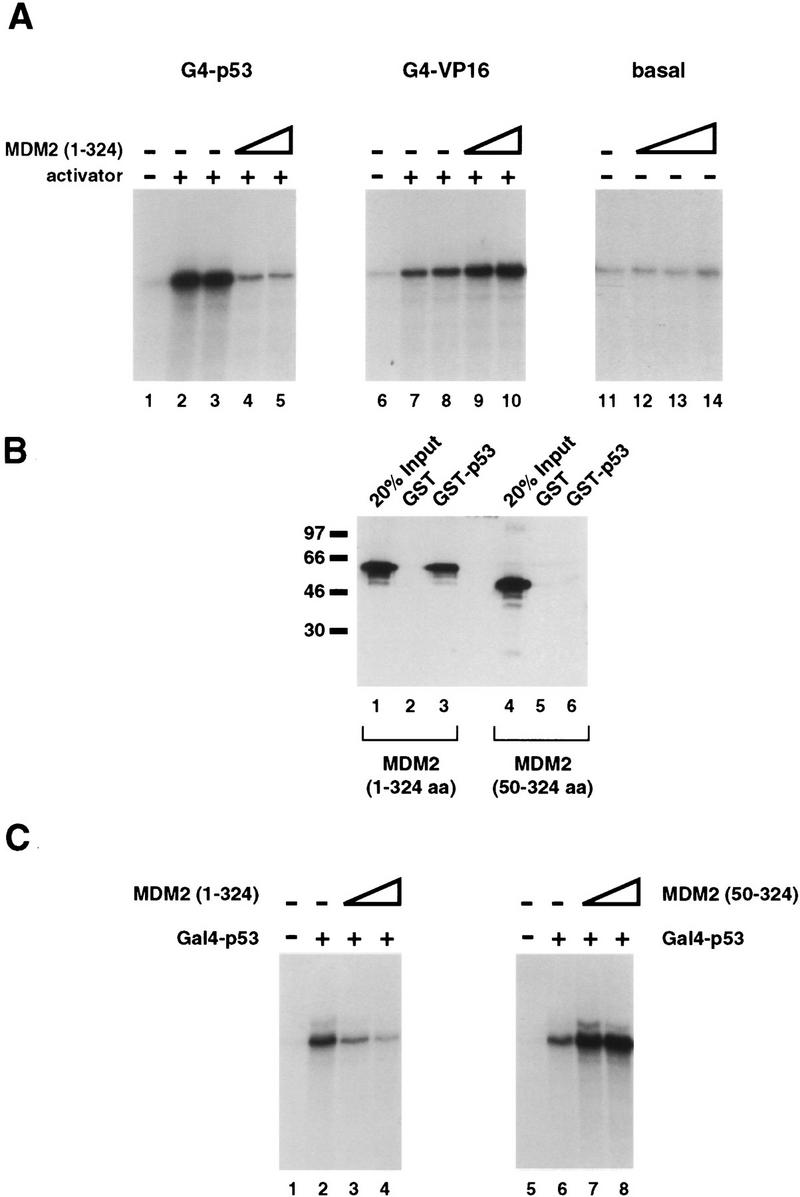
Development of an in vitro transcription system responsive to recombinant, human MDM2. (A) The first 324 amino acids of MDM2 specifically inhibit transcription dependent on the p53 activation domain in vitro. A protein containing the first 324 amino acids of human MDM2 was expressed and purified from bacteria and tested for its ability to inhibit transactivation by G4–p53, a protein consisting of the Gal4 DNA-binding domain (amino acids 1–94) fused to tandem copies of the p53 activation domain (amino acids 1–42). These proteins were assayed in an in vitro transcription system consisting of partially purified HeLa cell nuclear fractions and recombinant, purified hTFIIA using a template containing five Gal4-binding sites upstream the AdMLP. The promoter was fused to a G-less reporter, and the production of transcripts was measured by a G-less protocol. (Lane 1) The level of transcription in the absence of added activator; (lanes 2,3) reactions containing 30 ng of G4–p53. The reactions in lanes 4 and 5 contained both 30 ng of G4–p53 and 200 or 800 ng of purified, refolded MDM2(1–324), respectively. MDM2(1–324) was also tested for its ability to inhibit both basal transcription and transcription stimulated by the activation domain of VP16. (Lanes 7–10) 100 ng of a fusion protein consisting of the Gal4 DNA-binding domain (amino acids 1–147) and the activation domain of VP16 (amino acids 412–490). MDM2(1–324) protein was added to transcription reactions as follows, 200 ng (lanes 9,12), 400 ng (lane 13), or 800 ng (lanes 10,14). (B) The first 49 amino acids of MDM2 are required for an interaction with the activation domain of p53. GST (lanes 2,5) and a GST fusion protein containing amino acids 1–73 of p53 (lanes 3,6) were immobilized on glutathione resins and tested for their ability to retain soluble MDM2(1–324) (lanes 2,3) or an MDM2 protein lacking the first 49 amino acids [MDM2(50–324)] (lanes 5,6). After incubation with extracts containing the soluble MDM2 proteins, the resin and associated proteins were washed extensively, analyzed by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, probed with monoclonal antibodies against MDM2 (Pharmagenics), and detected using an ECL protocol (Amersham). Lanes 1 and 4 represent 20% of the amount of MDM2 protein added to the corresponding binding reactions. (C) MDM2(50–324), which cannot interact with p53, is unable to inhibit G4–p53 dependent transcription in vitro. Using the transcription system described in A, MDM2(1–324) and MDM2(50–324) were tested for their ability to inhibit G4–p53 transactivation. Lanes 1 and 5 contain no added activator; lanes 2 and 6 contain 30 ng of G4–p53. In addition to 30 ng of G4–p53, 60 and 200 ng of MDM2(1–324) and 60 and 200 ng MDM2(50–324) were added to lanes 3 and 4 and lanes 7 and 8, respectively.
