Figure 1.
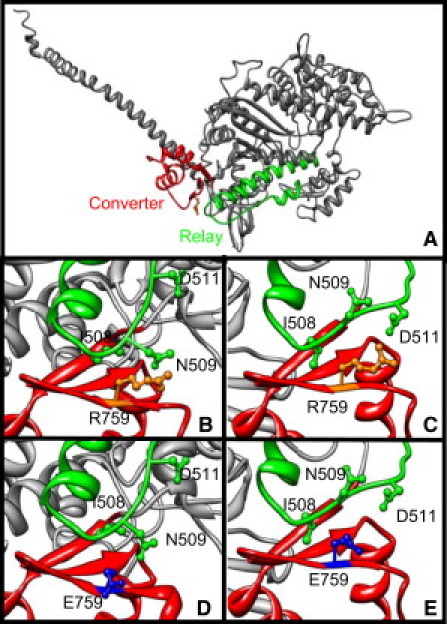
(A) Diagram of the mutant Drosophila IFM myosin heavy chain isoform (gray) showing the converter (red; residues 712–780 (12);) and relay (green; residues 469–525 (17)) domains in the prepower stroke state. (B) Close-up view of the wild-type, prepower stroke state of the relay and converter interface showing the three relay resides, I508, N509, and D511, with which converter residue R759 (gold) interacts (16,17). (C) Close-up view of the wild-type, postpower stroke state. (D) Close-up view of the mutant prepower stroke state showing the E759 converter mutation (blue). (E) Close-up view of the mutant postpower stroke state. Panels B–E are 90° counterclockwise rotated compared to panel A. Scallop myosin structures in the pre- and postpower stroke were used as templates and the Drosophila converter and relay amino acids substituted for the corresponding scallop residues (PDB codes 1QVI (4) and 1KK8 (6)). Molecular operating environment (MOE; http://www.chemcomp.com/software.htm) and UCSF CHIMERA (37) softwares were used to generate the figure.
