Figure 1.
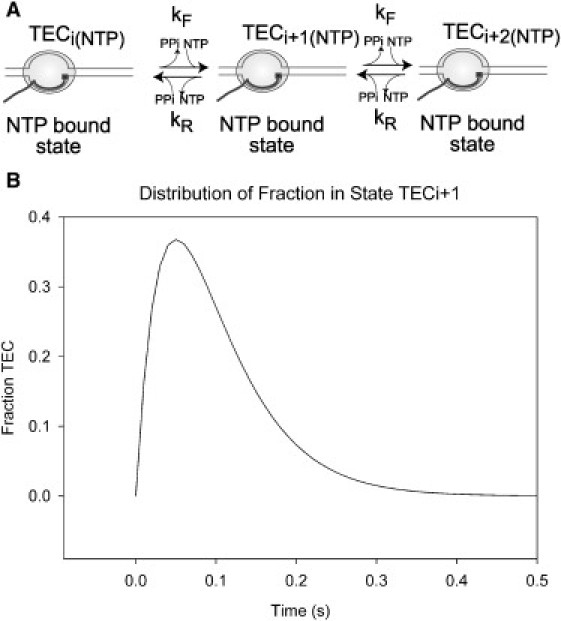
Simple model for transcription. (A) Depiction of a simple model for transcript elongation by a transcription elongation complex (TEC) across three template positions from the NTP-bound state at position (i) to position (i + 2), showing RNA polymerase (pale shaded oval), template DNA (fine lines), nascent RNA (dark line), and bound NTP (solid square). The events that occur during the forward reaction (NTP catalysis, pyrophosphate release, TEC translocation, and binding of the next templated NTP), or the reverse reaction (pyrophosphorolysis), are lumped together within the rate constants for the forward (kF) and reverse (kR) reactions between each position and represented by the reaction arrows. (B) Simulation of movement into, and out of, template position TECi+ 1 during transcription under standard conditions, using forward and reverse rate constants of 20 and 1 × 10−4 nt s−1, respectively. (Solid curve) Fraction of total TECs at position TECi+ 1 as a function of time.
