Figure 4.
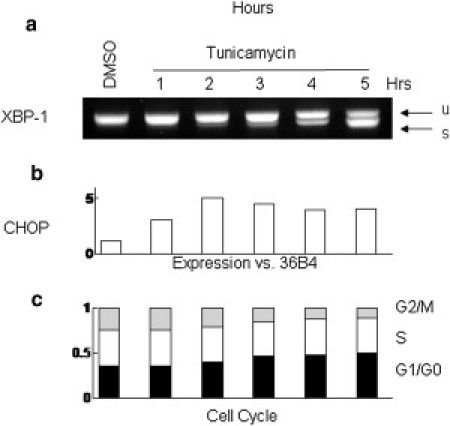
Molecular profile of H929 response to TM. The divergence in growth rates between the treated and untreated populations occurs synchronously with the up-regulation of the transcription factor CHOP (a) and the alternative splicing of transcription factor XBP1 (b) in the treated population. CHOP and XBP1-s activate a host of genes responsible for mitigating the effects of protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum. This is consistent with the known mechanism of TM action, an inhibitor of protein glycosylation. (c) Cell cycle data show a rapid reduction in the G2/M phase population and a corresponding increase in the G1/G0 population, consistent with cell cycle arrest. This shift becomes pronounced after 3 h of treatment, leaving 50% of cells in G1/G0 by the end of 5 h of treatment.
