Figure 1.
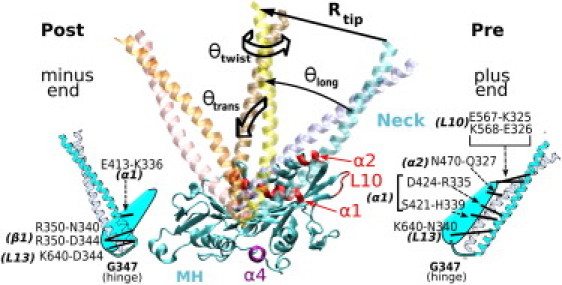
Major MH-neck contacts of Ncd in the pre- and post-stroke structures. Hydrophobic contacts (not shown) play a less specific role during the neck travel, and they are less conserved within the Kinesin-14 family (Table S2). We call the α-helical coiled-coil (α0) (A295-R346) the neck. The MT plus end is on the right. We measured the orientation of the neck using three angles, θlong, θtrans, and θtwist. Rtip is the distance of the tip of the neck (the S297 Cα atom) from its pre-stroke position. When the MH is bound to the MT, α1 is approximately parallel to the MT axis and guides the neck motion by forming intermediate contacts with it. The relay helix α4 mediates the nucleotide-dependent see-saw motion of the MH (Fig. S1) (52,53). Atomistic structures are rendered using VMD (59).
