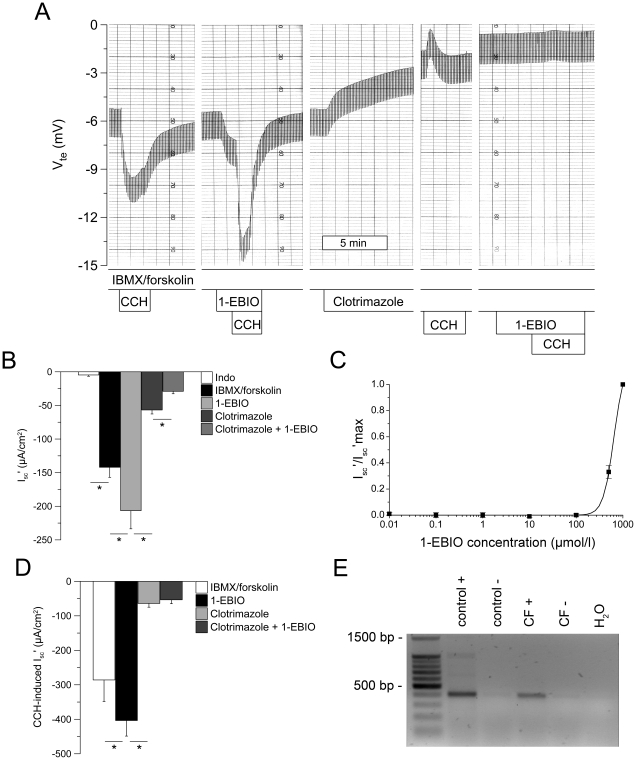
Figure 2. 1-EBIO potentiates cAMP-mediated and cholinergic Cl secretion in human rectal biopsies and this effect is abrogated by inhibition of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with clotrimazole.
(A) Original recording of effects of 1-EBIO (500 µM, basolateral) on cAMP-induced Cl− secretion (IBMX/forskolin) and cholinergic co-activation (CCH), and effects of clotrimazole (30 µM, basolateral) on Cl− secretory responses in a rectal biopsy from a control subject. Experiments were performed in the presence of amiloride, indomethacin and IBMX/forskolin. (B) Summary of effects of 1-EBIO on cAMP-induced Cl− secretion and inhibition by clotrimazole in rectal tissues from control subjects. (C) Concentration-response curve for 1-EBIO-induced Cl− secretion was determined in the presence of cAMP-mediated activation (IBMX/forskolin). (D) Effects of 1-EBIO on CCH-induced Cl− secretion in the presence of IBMX/forskolin and inhibition by clotrimazole in control rectal tissues. Data are presented as mean±SEM. n = 17 individuals per group. *P<0.001. (E) RT-PCR analysis revealed transcripts of the clotrimazole-sensitive Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCNN4 in rectal biopsies from control and CF subjects. The 405 bp KCNN4 fragment was only identified in the presence (+), but not in the absence of reverse transcriptase (-).