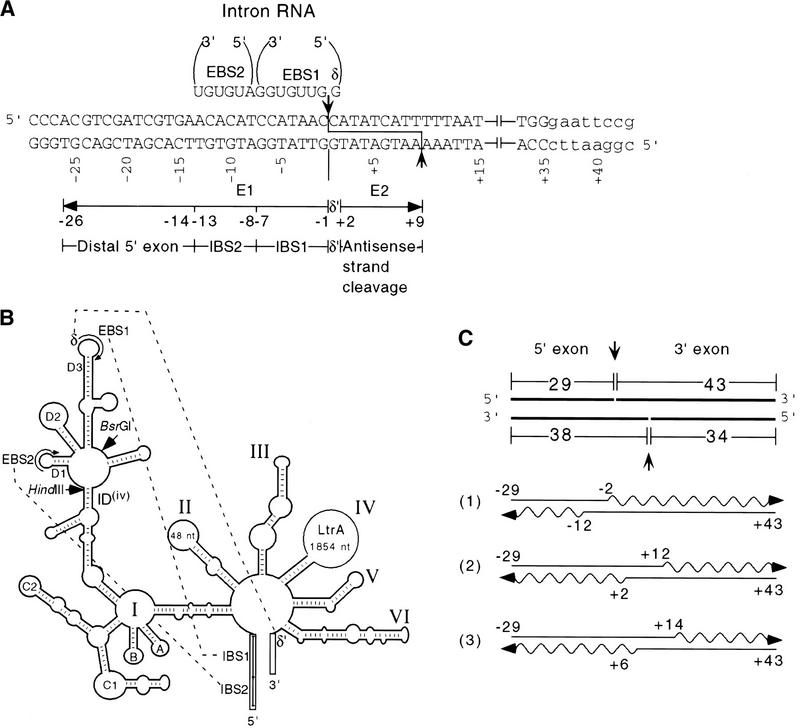
Figure 1.
Target site and intron interactions. (A) DNA target site and EBS–IBS and δ–δ′ interactions. Partial sequence of the 72-bp DNA target site used for biochemical assays is shown. Uppercase letters indicate ltrB sequence, and lowercase letters indicate the 3′ EcoRI site added for cloning. The intron RNA's EBS1, EBS2, and δ sequences that potentially base-pair with the target DNA are shown at top. The positions of the intron–insertion site (top strand) and antisense-strand cleavage site (bottom strand) are indicated. (B) Schematic of the Ll.LtrB intron showing base-pairing interactions with flanking exon sequences (EBS1–IBS1, EBS2–IBS2, δ–δ′). (C) Synthesis of DNA substrates. 32P-Labeled DNA substrates were synthesized by annealing overlapping DNA oligonucleotides (straight lines) and then using Sequenase to fill in single-stranded regions in the presence of a 32P-labeled dNTP (wavy lines). (Top) The 72-bp DNA substrate with the arrows indicating the intron–insertion site (top strand) and antisense-strand cleavage site (bottom strand). (1) oligonucleotides used to introduce mutations into the distal 5′ exon and 3′ exon regions of the DNA target site; (2) oligonucleotides used to introduce IBS and δ′ mutations; (3) oligonucleotides used to introduce mutations between positions +1 and +5 in Fig. 6B. The bubble substrates were made by using the bottom strand oligonucleotide from pair 1 and the top strand oligonucleotide from pair 3 with appropriate mutations (Fig. 6).