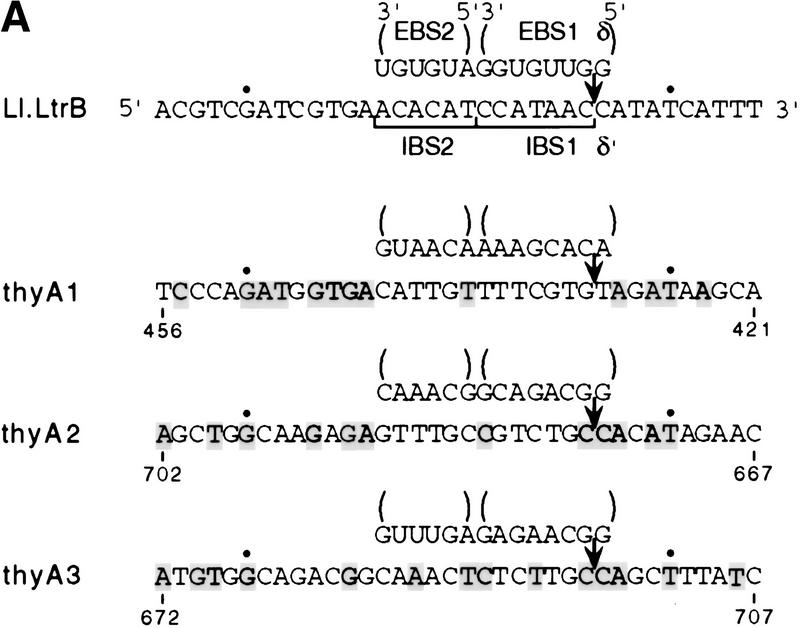
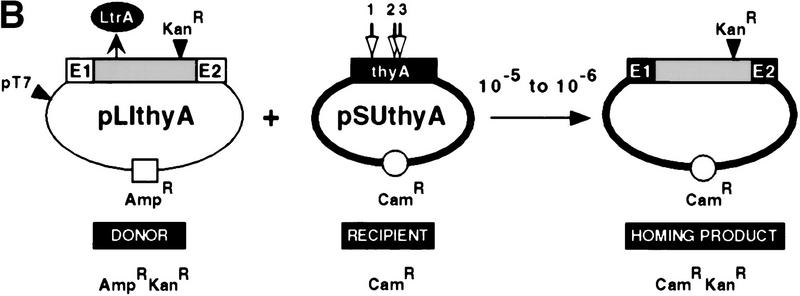
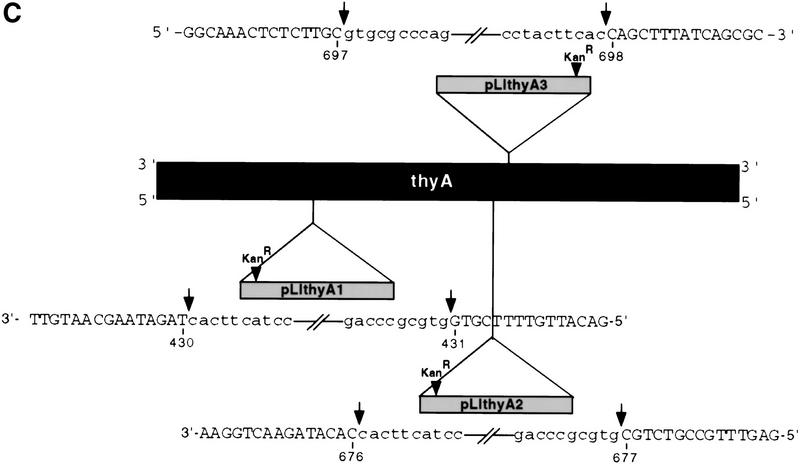
Figure 8.
Retargeting of the Ll.LtrB intron to the thyA gene. (A) Sequences of thyA target sites and potential base-pairing interactions with the retargeted introns. The wild-type ltrB target site and base-pairing interactions with the wild-type Ll.LtrB intron are shown at top. Nucleotides in the thyA target sites that match those in the wild-type ltrB site are shaded. Dots above G-21 and T+5 correspond to critical residues representing the two fixed positions in the search for new target sites. The arrow indicates the intron–insertion site. (B) Mobility assay with retargeted introns. The retargeted introns were expressed from pLIthyA derivatives of the AmpR donor plasmid pLI1KR′ and have a KanR resistance marker in domain IV. The CamR-recipient plasmid pSUthyA contains the E. coli thyA coding sequence in place of the ltrB target site in pSU18. The locations of the thyA1, thyA2, and thyA3 target sites in the thyA gene are indicated by arrows. Insertion of the retargeted intron into the thyA target site was detected by a CamRKanRAmpS phenotype and confirmed by PCR analysis and restriction digests. (C) DNA sequence analysis of intron–insertion sites in mobility products. Intron–exon boundaries were amplified by PCR, using the forward and reverse sequencing primers in conjunction with primers near the 5′ and 3′ ends of the intron, and the PCR products were sequenced. The thyA3 site is in the top strand, whereas the thyA1 and thyA2 sites are in the bottom strand. Uppercase and lowercase letters indicate exon and intron sequences, respectively; arrows indicate intron–exon junctions.