Figure 5.
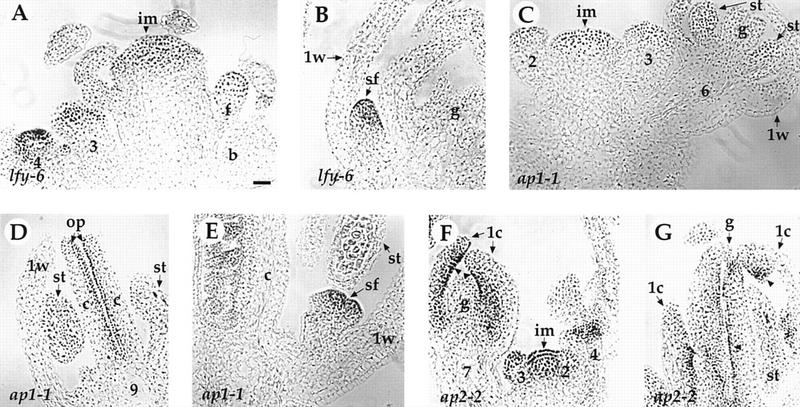
Expression of the PAN protein in lfy, ap1, and ap2 mutants. (A–B) lfy-6. (A) PAN protein is expressed in the inflorescence meristem (im) and the center of abnormal young flowers. The stages of flowers (3 and 4) and the floral bud (f) in the axil of the bract (b) are indicated. (B) PAN protein is detected in the secondary floral buds (sf) in the axils of the first-whorl organs (1w) of an old lfy-6 flower. (g) Gynoecium. (C–E) ap1-1. (C) Early expression in the inflorescence meristem (im) and in the stage 2, 3, and 6 floral buds is normal (compared with Figs. 4D–F). (st) Stamen. (D) PAN protein is expressed normally in the ovule primordia (op) at stage 9 flowers (cf. with Fig. 4G). (c) Carpel. (E) Secondary floral buds (sf) in the axil of the first-whorl organs (1w) show PAN protein expression at levels comparable to the early flower primordia arising on the inflorescence apex (Figs. 4D,E). (F–G) ap2-2. PAN protein expression is largely normal in the inflorescence meristem (im) and young floral buds (stage 2–4). At later stages, PAN protein is detected in the ovule primordia (arrowhead) in both of the first-whorl carpels (1c) and the central gyneocium (g). The number indicated corresponds to the developmental stage of each flower (Smyth et al. 1990). Bar, 20 μm.
