Fig. 5.
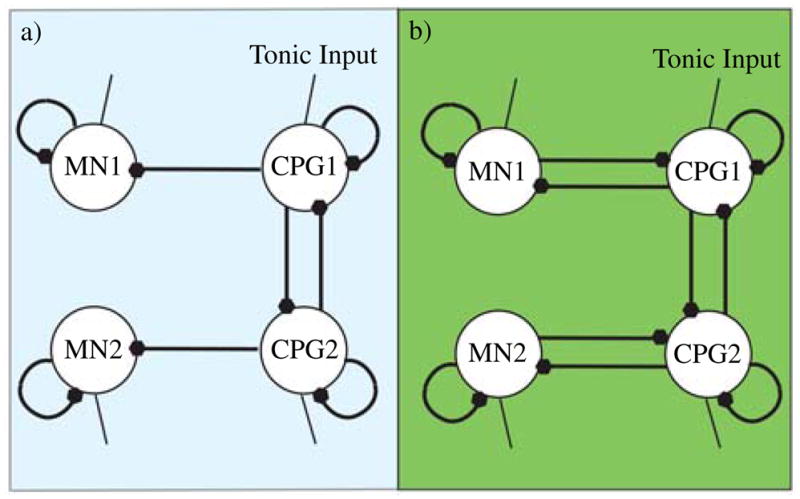
Reduced canonical network for (a) software simulations and (b) hardware simulations. Similarities and symmetries between neural outputs allow CPG1 and CPG2 to act as the half-centered oscillator as well as the hip extensors (CPG1-left hip, CPG2-right hip), and flexors (CPG1-right hip, CPG2-left hip). Further 180° symmetry between legs allows the motor neurons to function as both knee extensors (MN1-left knee, MN2-right knee) and flexors (MN1-right knee, MN2-left knee). The additional coupling between the motor and CPG neurons in the hardware implementation allows for greater flexibility and control of the gait. For nonsymmetric gaits, the network would be expanded to allow independent control of the left and right motor neurons.
