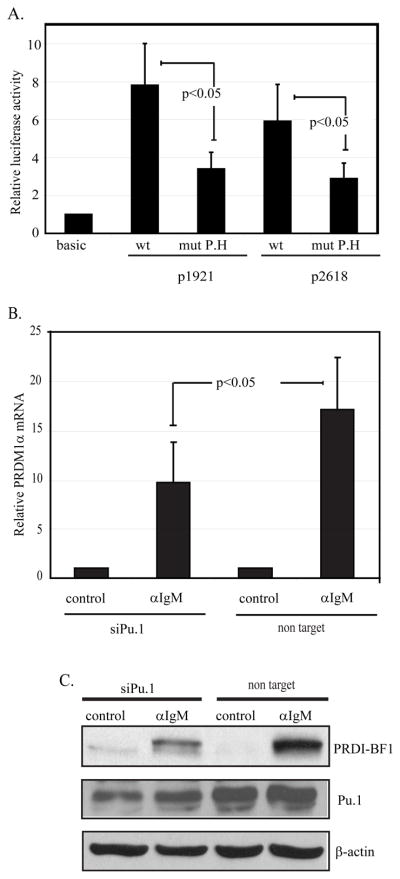
Figure 7. Site P.H and transcription factor PU.1 are involved in anti-IgM-mediated transcriptional activation of PRDM1.
A) The p1921 and p2618 PRDM1 promoter-luciferase constructs containing a wild type or mutated sequence at the P.H site were transfected into CA46 cells. Mutation of the P.H site in either construct decreased promoter activity. The mutation is the same as shown in figure 6A. The lane marker “basic” represents the activity from the promoterless vector, pGL3-Basic. Promoter activity was normalized as in figure 3 and represents six independent experiments with SEM shown. B) Endogenous PRDM1 expression is inhibited by loss of PU.1. CA46 lymphoma cells transfected with either non targeting control siRNA or an siRNA specific to PU.1 for twenty four hours and then either stimulated with anti-IgM (αIgM) or untreated (control) for an additional twenty four hours. PRDM1 mRNA was assessed by quantitative RT-PCR. Data was normalized to GAPDH and shown as fold induction relative to untreated (control) sample. Data is the mean of 3 independent experiments with SEM shown. C) Immunoblot analysis of PU.1 and PRDI-BF1 expression. PU.1 siRNA decreased PU.1 protein levels and diminished induction of PRDI-BF1 in response to anti-IgM. Experimental conditions are as in panel B.