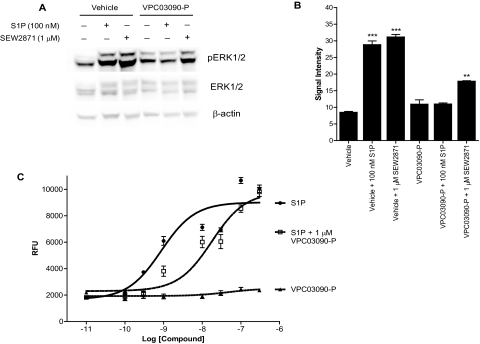
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of signaling targets downstream of S1P receptors. A, Western blot to detect phosphorylation state of ERK1/2 in CHO cells expressing human S1P1. Cells were serum-starved for 16 h, then incubated with 10 μM VPC03090-P or vehicle for 1 h, and then stimulated where indicated by 100 nM S1P or 1 μM SEW2871 for 5 min. A standardized protein amount of 128 μg was loaded in all lanes. The experiment was performed in duplicate for all conditions with representative results shown here. B, quantification of signal intensity for pERK1/2 bands detected on Western blot. Signal intensity of phosphorylated ERK1/2 protein bands detected by infrared imaging as described under Materials and Methods was quantified using Odyssey Infrared Imaging software (LI-COR, Inc.) and presented here in arbitrary units. Each column bar represents the average of a duplicate, and error bars depict the S.E.M. Results were analyzed for statistical significance within Prism software by performing a one-way ANOVA test, followed by a Newman-Keuls multiple comparison post-test. **, p < 0.01 for VPC03090-P + 100 nM S1P versus VPC03090-P + 1 μM SEW2871 comparison. ***, p < 0.001 for vehicle + 100 nM S1P versus vehicle comparison, and separately, vehicle + 1 μM SEW2871 versus vehicle comparison. C, results from a Ca2+ mobilization assay using CHO cells expressing human S1P3. Relative fluorescence units (RFU) indicate the amount of fluorescence produced from a Ca2+-sensing fluorophore in response to a concentration range of applied S1P, VPC03090-P, or coapplication of S1P and a fixed concentration of VPC03090-P. Each data point represents the average of a quadruplicate, with the error bars indicating the S.E.M..