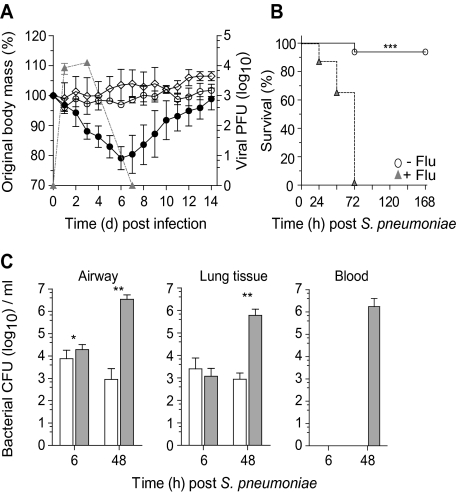
Figure 1.
Influenza infection increases susceptibility to Streptococcus pneumoniae superinfection. A, Body mass (left axis) and viral titer (triangles, right axis) of wild-type C57BL/6 mice infected with 1.25 × 105 plaque-forming units (PFU) of A/HK/X31 influenza (closed circle), 104 colony-forming units (CFU) Streptococcus pneumoniae (open circle), or vehicle control (diamonds). B, Survival of naive (open circle) or day 7 influenza-infected (triangles) wild-type mice infected with 104 CFU S. pneumoniae. C, Viable bacterial CFU recovered from the airway, lung tissue, and peripheral blood of naive (open bar) or day 7 postinfluenza (gray bar) mice at 6 hours and 48 hours following 104 CFU S. pneumoniae. Two-way ANOVA was used to interrogate weight loss, survival differences were determined using the log-rank Mantel–Cox test, and all other data were tested using a 2-tailed Mann–Whitney t test with 95% confidence intervals. Data are representative of 4 independent experiments (n = 5 mice per group). * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001 versus corresponding group.