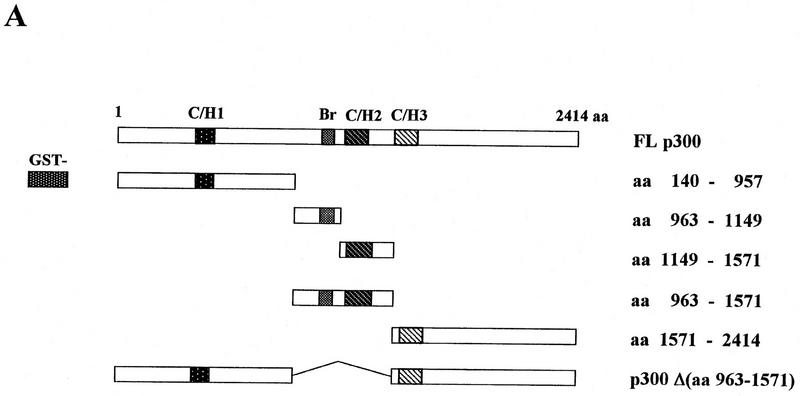
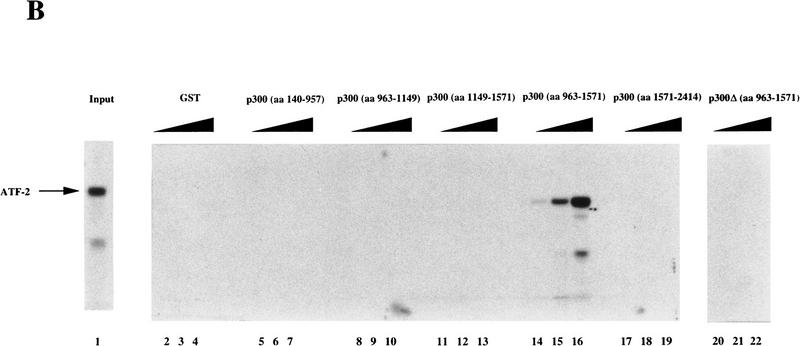
Figure 3.
Interaction of in vitro-translated ATF-2 with deletion variants of GST–p300. (A) Schematic representation of the variants of GST–p300. Shown are p300 and deletion derivatives fused to the GST protein. The patterned boxes represent the cysteine/histidine-rich regions C/H1, C/H2, and C/H3, and are labeled; (Br) The bromodomain. The numbers at right indicate the amino acids of p300. (FL p300) Full-length p300 protein; [p300Δ(amino acids 963–1571)], p300 protein lacking amino acids 963–1571; (GST) glutathione S-transferase–truncated protein. (B) In vitro translated [35S]methionine-labeled ATF-2 was incubated with the GST–p300 variants that consisted of the amino-terminal, carboxy-terminal, and central portions of the protein (lanes 5–19) or variants that lacked amino acids 963–1571 (lanes 20–22), or ATF-2 was incubated with GST alone (lanes 2–4). The bound ATF-2 is indicated by an arrow at left. (Lane 1) Input, namely, in vitro-translated [35S]methionine-labeled ATF-2. The input lane contained 1.5% (in terms of cpm) of the radiolabeled protein used in the binding experiments.