Figure 7.
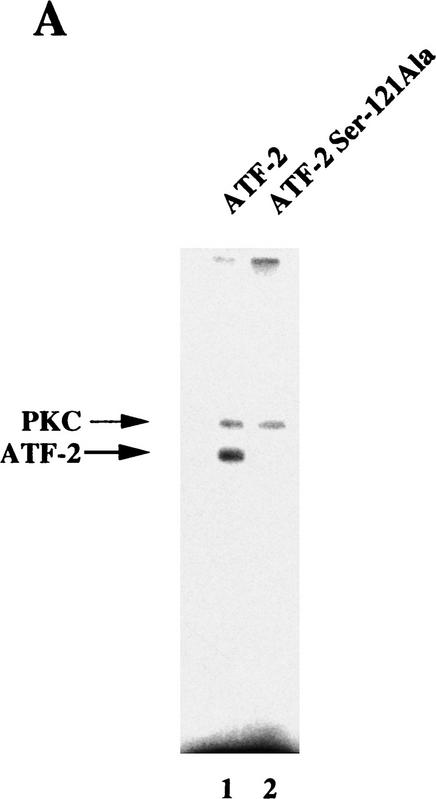
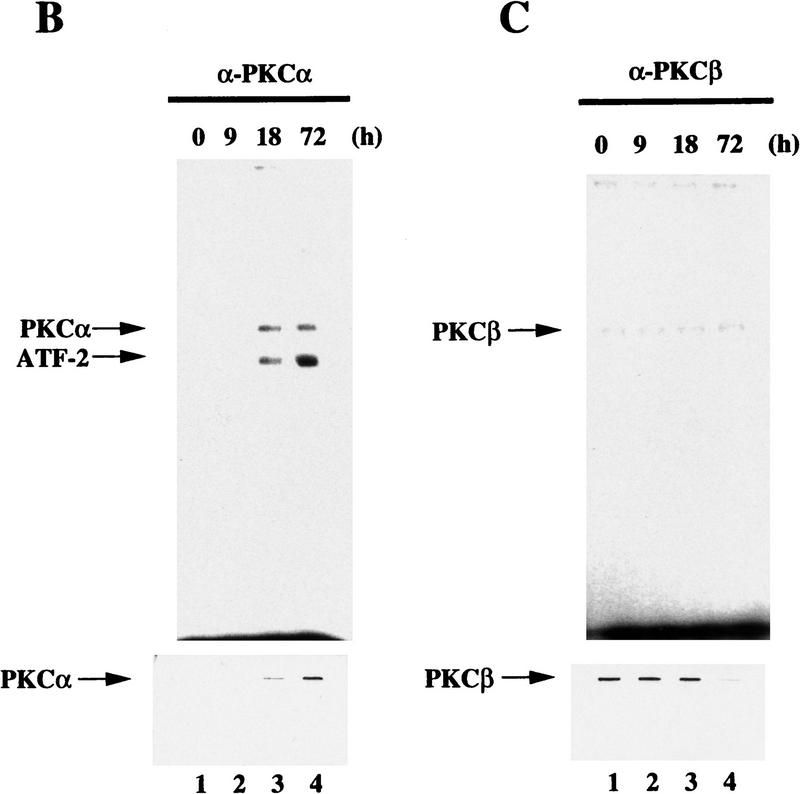
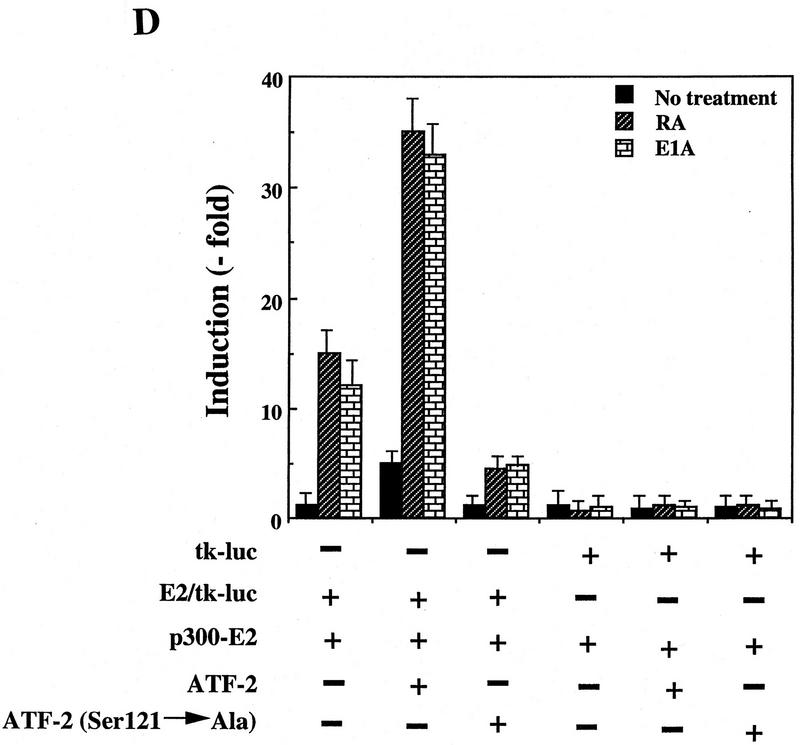
ATF-2 is phosphorylated by PKC and activates a p300–E2 fusion protein. (A) Five micrograms of ATF-2 and mutant ATF-2Ser121–Ala proteins were purified from E. coli and incubated with 25 ng of a mixture of recombinant PKCα, PKCβ, and PKCγ mixture in the appropriate kinase buffer (see Materials and Methods) for 10 min at 30°C. The resultant phosphorylated proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide). (Lane 1) ATF-2; (lane 2) ATF-2Ser121–Ala mutant protein. (B,C) F9 cells were incubated with 3 × 10−7 m RA for the indicated periods of time. Nuclei were isolated and nuclear lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with polyclonal antibodies specific for PKCα (B) and PKCβ (C), respectively, and protein A–Sepharose for 2 hr at 4°C. The immune complexes were incubated with 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP in kinase buffer for 30 min at 30°C. The resultant phosphorylated protein complexes were subjected to SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide). (Lane 1) F9 cell extract; (lanes 2–4) F9 cells lysate that had been incubated with RA for 9, 18, and 72 hr, respectively. The immunoprecipitates with antibodies specific for PKCα or PKCβ were immunoblotted with the antibodies against the respective PKC (bottom panels). (D) F9 cells that had been stably transfected with 5 μg of tk–luc or 5× E2/tk–luc were cotransfected with 3 μg of pCMV–p300–E2 with or without 4 μg of pCMV–ATF-2 or 4 μg of pCMV–ATF-2Ser121–Ala plus 2 μg of pRSV-LacZ, as indicated. The cells were incubated for 72 hr in the absence or presence of 3 × 10−7 m RA or 2.5 μg of pCMV–E1A. The results are expressed as the extent of induction (x-fold) as compared to the results with the control plasmid (pcDNA3). The results are the means from three independent experiments.