Figure 7.
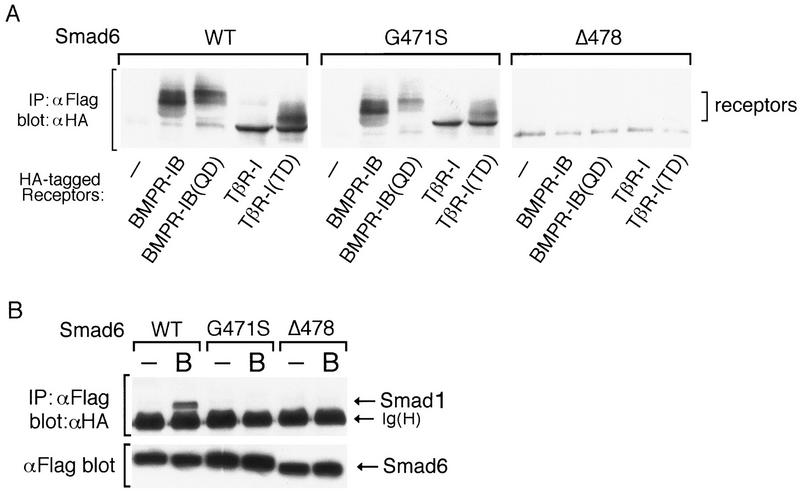
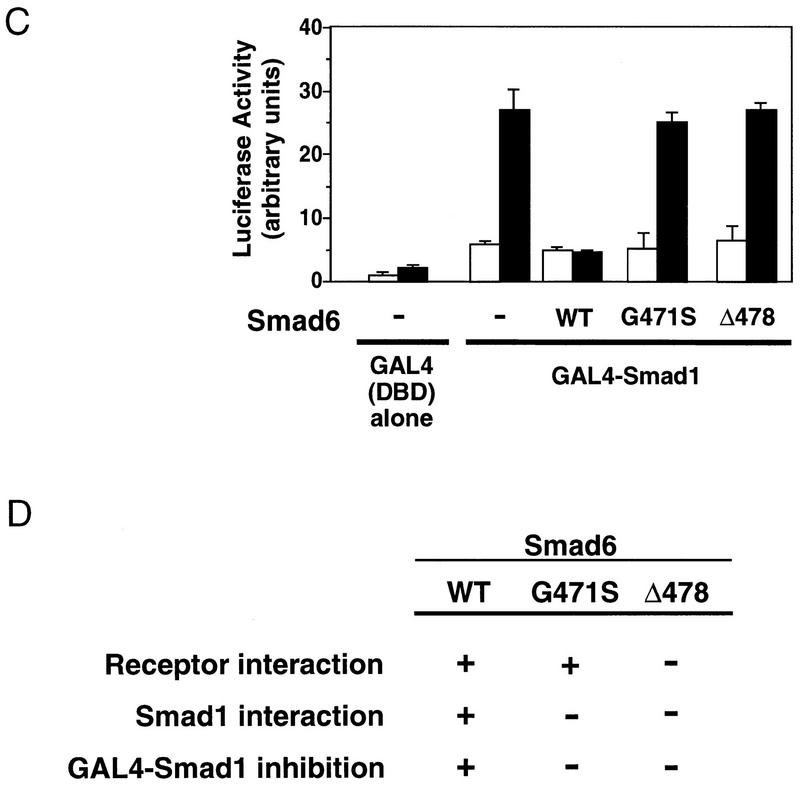
The inhibitory activity of Smad 6 segregates with its ability to interact with Smad1. (A) Smad6(G471S) interacts with the type I receptors of TGFβ family. Flag-tagged wild-type Smad6 (WT) or two different mutants (G471S and Δ478) were cotransfected into COS cells with HA-tagged wild-type or constitutively active type I receptor (QD and TD) for BMPs (BMPR-IB) or TGFβ (TβR-I). Cell lysates were subjected to anti-Flag immunoprecipitation using a monoclonal antibody followed by immunoblotting using anti-HA polyclonal antibody. Similar levels of receptor and Smad6 expression were confirmed (data not shown). (B) Smad6 mutants fail to interact with Smad1 on BMP stimulation. Flag-tagged wild-type Smad6(WT) or mutants (G471S and Δ478) were cotransfected into COS cells with HA-tagged Smad1. Cell lysates were subjected to anti-Flag immunoprecipitation using a monoclonal antibody followed by immunoblotting using anti-HA polyclonal antibody (top panel). Similar levels of receptor and Smad6 expression were confirmed by anti-Flag Western blot (bottom panel). (C) Smad4 prevents Smad6 from inhibiting Smad1. R1B/L17 cells were transfected with the reporter gene (GAL4–lux, 1 μg), BMPR-IB (1 μg), BMPR-II (0.1 μg) and either a vector containing the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (DBD) alone or a GAL4(DBD)–Smad1 fusion construct. Smad6 (2 μg) and/or Smad4 (4 μg) were cotransfected where indicated. Cells were incubated with (solid bar) or without (open bar) 5 nm BMP2 for 18 hr. Luciferase activity is expressed as the mean ± s.d. of two independent experiments. (D) Summary table of the activities of Smad6 mutants.