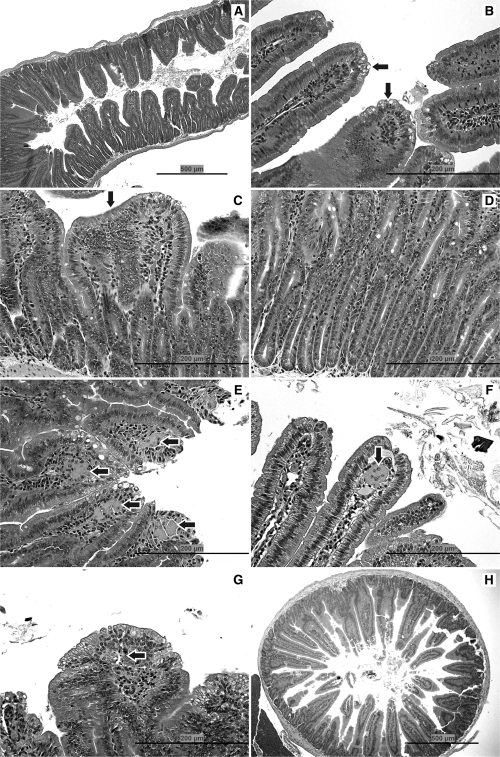
FIG. 1.
Pathology. (A) Duodenum of mouse exposed to 520 mg/l SDD for 8 days: with villous atrophy, blunting and fusion, and crypt epithelial hyperplasia. (B) Jejunum of mouse exposed to 170 mg/l SDD for 8 days: with cytoplasmic vacuolization of the villous epithelium (arrows). (C) Duodenum of mouse exposed to 520 mg/l SDD for 90 days: with villous atrophy, blunting and fusion (arrow), and crypt epithelial hyperplasia. (D) Duodenum of mouse exposed to 520 mg/l SDD for 90 days: with crypt epithelial hyperplasia. (E) Duodenum of mouse exposed to 520 mg/l SDD for 90 days: with histiocytic cellular infiltration of the villous lamina propria (arrows) and cytoplasmic vacuolization of the villous epithelium. (F) Jejunum of mouse exposed to 170 mg/l SDD for 90 days: with a multinucleate syncytium in the villous lamina propria (arrow). (G) Duodenum of mouse exposed to 520 mg/l SDD for 90 days: with apoptosis in the lamina propria (arrow) and cytoplasmic vacuolization of the villous epithelium. (H) Duodenum of a control mouse on day 91.