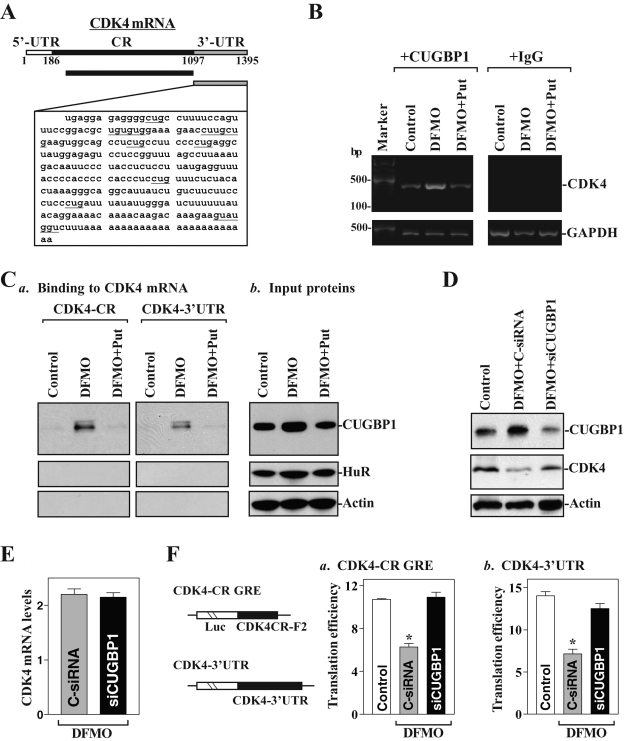
FIGURE 4:
Binding of cytoplasmic CUGBP1 to CDK4 transcripts and its regulatory effect on CDK4 translation in polyamine-deficient cells. (A) Schematic representation of CDK4 mRNA and the GU-rich sequences in its 3′-UTR. (B) Association of endogenous CUGBP1 with endogenous CDK4 mRNA was tested by RNP IP analysis; RNA was isolated, and RT-PCR products of CDK4 were examined by RT-PCR analysis. (C) Representative CUGBP1 immunoblots after pull-down using biotinylated CDK4 CR (a, left) or 3′-UTR transcripts (a, right) and cytoplasmic lysates and input proteins (b). β-actin, negative control in pull-down materials. (D) Effect of CUGBP1 silencing on CDK4 protein expression levels. Whole-cell lysates were harvested 48 h after cells were transfected with either control siRNA (C-siRNA) or siCUGBP1. (E) Levels of total CDK4 mRNA in polyamine-deficient cells after CUGBP1 silencing as measured by Q-PCR analysis. Values are means ± SE of data from three samples. (F) Changes in CDK4 translation efficiency as measured by analysis of CDK4-CR GRE or CDK4 3′-UTR luciferase reporter (schematic), after cotransfection with a Renilla luciferase reporter. Values are means ± SE of data from three separate experiments. *p < 0.05 compared with controls and cells exposed to DFMO plus Put.