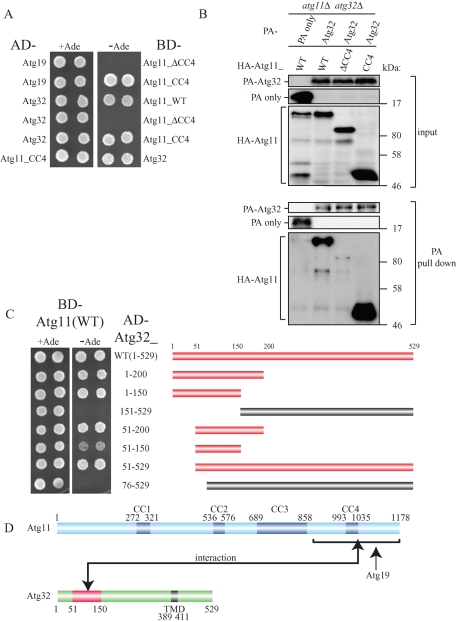
FIGURE 1:
The N-terminus region (51–150) of Atg32 interacts with the C-terminus region of Atg11. (A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis between Atg19 and Atg11 mutants, and between Atg32 and Atg11 mutants. The PJ69-4A strain was transformed with pGAD and pGBD plasmid, which can express the indicated proteins. Cells were grown on +Ade or –Ade plates at 30°C for 4 d. (B) The C-terminus region of Atg11 associated with Atg32 during nitrogen starvation. The atg11Δ atg32Δ strains expressing PA-tagged Atg32 or PA only and the indicated HA-tagged Atg11 mutants under the control of the CUP1 promoter were grown in SMD medium until the mid–log phase and then starved in SD-N for 1 h. PA-Atg32 was precipitated using IgG–Sepharose from cell lysates. Top two, an immunoblot of total-cell lysates. Bottom two, the IgG precipitates, which were probed with anti-HA and anti-PA antibodies. (C) Yeast two-hybrid analysis between Atg11 and the indicated Atg32 mutants (left). Each bar indicates expressed Atg32 mutants (right). Red bars indicate yeast two-hybrid positive and the gray bars indicate yeast two-hybrid negative. (D) Schematic drawing of Atg11 and Atg32. Atg11 is predicted to have a fourth coiled-coil domain (CC1–CC4). Atg32 has a TMD. The domain of Atg32 required for Atg11 interaction as determined by yeast two-hybrid study is highlighted in red.