Figure 4.
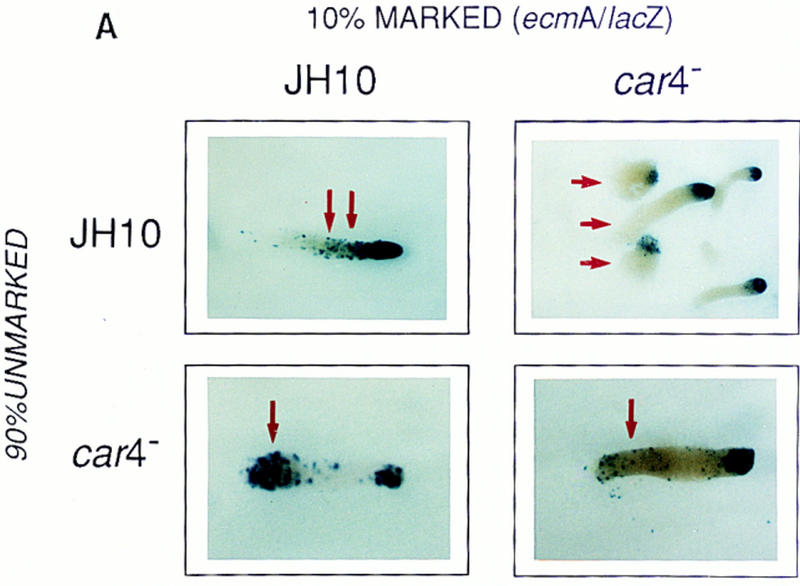
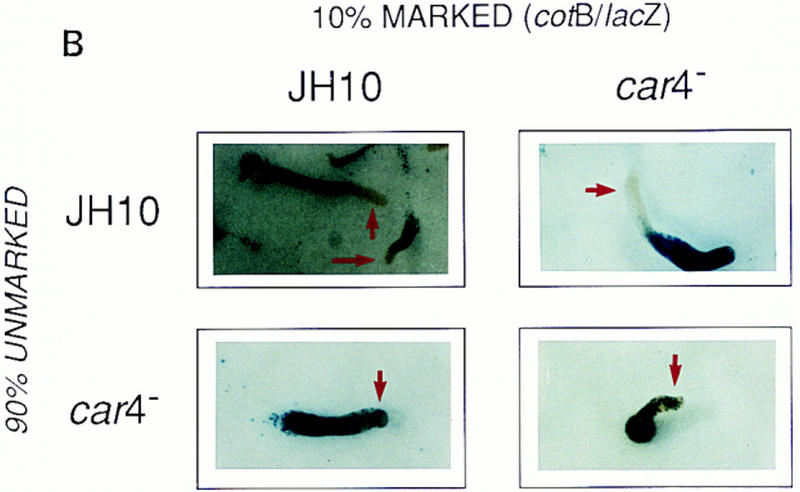
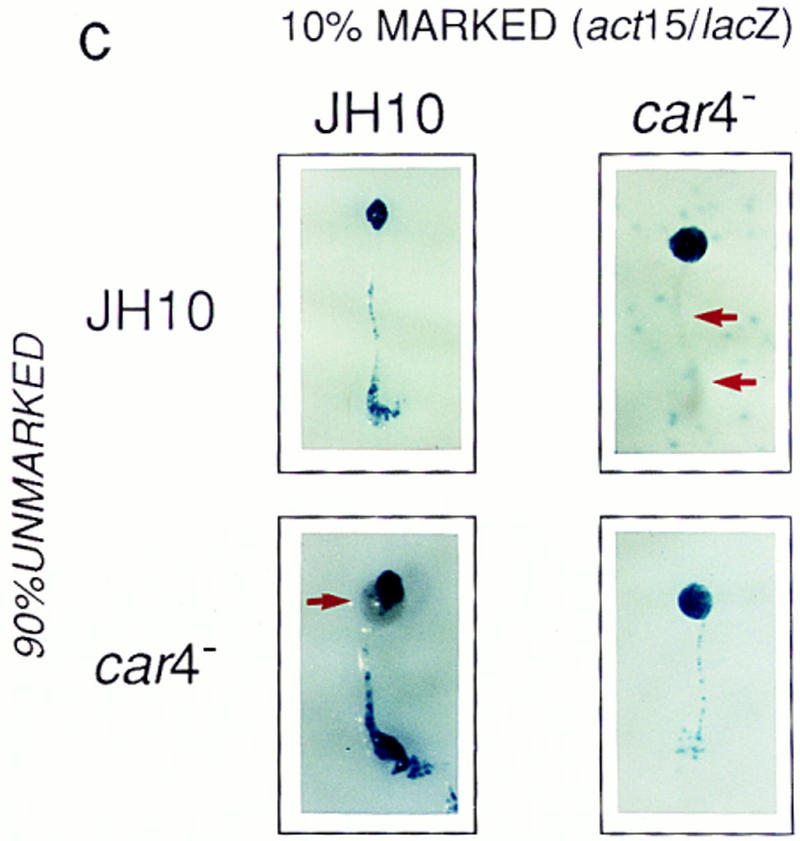
Patterning in developmental chimeras. (A) Chimeras with ecmA/lacZ marked cells. β-Galactosidase staining of various chimeric mixes of unmarked cells and cells carrying the prestalk ecmA/lacZ transgene at 9:1 ratios, respectively, as indicated. Arrows depict differences in prestalk ALC staining in slug posteriors among the different chimeras. (B) Chimeras with cotB/lacZ marked cells. β-Galactosidase staining of various chimeric mixes of unmarked cells and cells carrying the prespore cotB/lacZ transgene at 9:1 ratios, respectively, as indicated. Arrows depict differences in prespore staining in the slug anteriors among the different chimeras. (C) Chimeras with act15/lacZ-marked cells. β-Galactosidase stainings of various chimeric mixes of unmarked cells and cells carrying the ubiquitous act15/lacZ transgene at 9:1 ratios, respectively, as indicated. Arrows depict differences in staining of fruiting bodies among the different chimeras. car4− cells fail to populate the stalk when mixed with wild-type JH10 cells. JH10 cells fail to form spores when developed with car4 null cells but contribute primarily to the stalk tube and and prestalk derived upper cup that is localized atop the spore mass.
