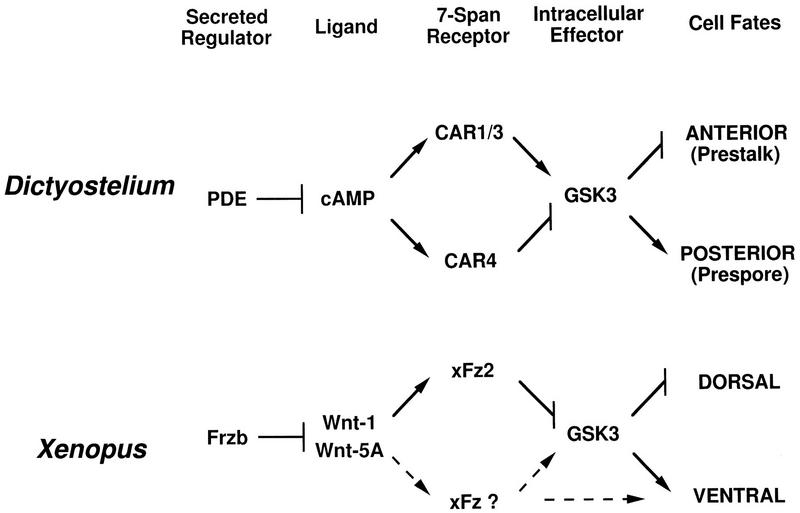
Figure 9.
Parallel pathways for axes formation in Dictyostelium and Xenopus. In Dictyostelium, PDE will degrade the secreted morphogen cAMP, which will activate the CAR family. CAR4 and CAR1/3 act antagonistically and converge at GSK3. High GSK3 levels promote prespore differentiation and inhibit prestalk patterns. LiCl will stimulate prestalk differentiation through inhibition of GSK3. In Xenopus, the Frzb family of secreted proteins can bind Wnt morphogens with high affinity. Activation of Xenopus Fz2-type receptors during early embryogenesis by the Wnt-1 class down-regulates GSK3 activity and stimulates dorsal structures. The Wnt-5A class will antagonize the dorsalizing action of Wnt-1. Broken lines indicate potential pathways for ventral activation via another Fz receptor. Direct activation of GSK3 is suggested by comparison with CAR signaling in Dictyostelium (see above).