Figure 3.
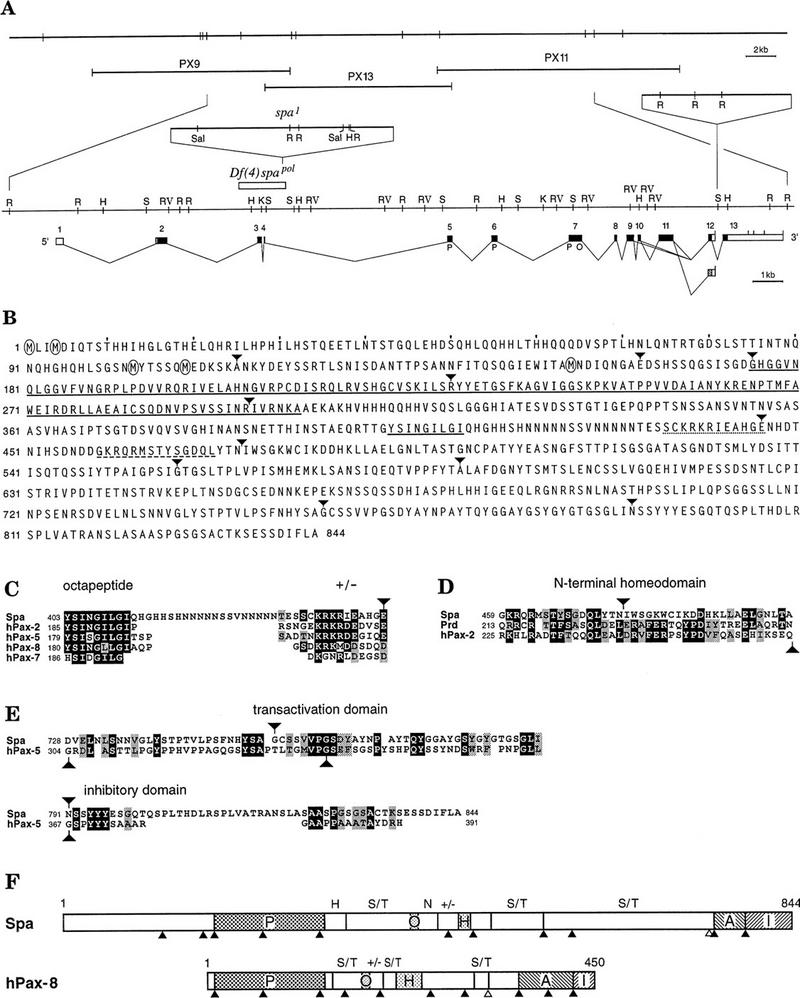
Structural organization of the spa locus and deduced sequence and conserved domains of the Spa protein. (A) The spa locus is shown with respect to a genomic EcoRI map at the top and three overlapping inserts from a λ DASH II genomic library below. Underneath, an enlarged detailed restriction map of the genomic region spanning the spa transcript is shown, above which two spa mutations, the spa1 insertion and the spapol deficiency, and an insertion polymorphism in intron 12 are indicated. Below the restriction map, the intron–exon structure and the open reading frame (in black; with paired domain P and octapeptide O) corresponding to the longest spa cDNAs from embryos and third instar larvae are depicted, and different splice variants are indicated. In third instar larvae, only two splice variants, which differed with respect to the presence or absence of exon 11, were detected by reverse transcriptase PCR amplification of total disc RNA. Both used the poly(A) addition site in intron 12 and therefore, lacked the putative inhibitory domain encoded by exon 13. Occasionally, an alternative 3′ splice acceptor site of intron 9 is used, resulting in the in-frame deletion of the first two amino acids encoded by exon 10. Abbreviations of restriction sites: (H) HindIII; (K) KpnI; (R) EcoRI; (RV) EcoRV; (S) SpeI; (Sal) SalI. (B) The deduced amino acid sequence of the longest open reading frame encoded by spa cDNAs with encircled methionines indicating the positions of the five potential initiators preceding the paired domain. Underlined are the paired domain and octapeptide by solid lines, a conserved highly charged dodekapeptide by a dotted line, and a peptide homologous to the amino terminus of a homeodomain by a dashed line. (C–E) The conservation of the octapeptide and highly charged dodekapeptide sequences (C), of the fractional homeodomain sequences (D), and of the carboxy-terminal transactivation and inhibitory domains of Pax2, Pax5, and Pax8 and Spa (E). (F) The conservation of domains and positions of introns in Spa and Pax2, Pax5, and Pax8 proteins. The position of introns are indicated by filled triangles, alternative splice sites by open triangles in Spa and human Pax8. In addition to the paired domain (P), octapeptide (O), amino-terminal portion of a homeodomain (H), transactivation domain (A), and inhibitory domain (I), Ser/Thr-rich domains (S/T), Gln-rich domains (N), and highly charged regions (+/−) are indicated.
