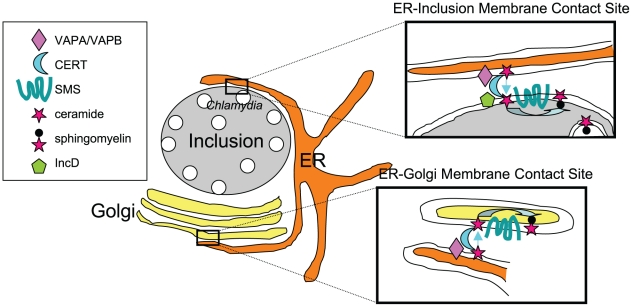
Figure 1. Direct transport of ceramide from the ER to C. trachomatis inclusion.
At ER-Golgi membrane contact sites the ceramide transfer protein CERT associates to the ER-resident proteins VAPA/VAPB and, via its PH domain, to PI4P at the trans-Golgi. Upon transfer by CERT, ceramide is converted to SM by a SM synthase (SMS). In Chlamydia-infected cells, ER-inclusion membrane contact sites involving VAPA/VAPB and CERT are observed. CERT interacts with the inclusion-anchored bacterial protein IncD through its PH domain but independently of PI4P. Upon transfer to the inclusion membrane, ceramide might be converted to SM by host SMS, which is enriched around the inclusion, and incorporated by the bacteria. Because the catalytic site of SMS is in the lumenal site of the Golgi apparatus, it would imply that the enzyme traffics to the inclusion membrane to convert ceramide, by a mechanism that remains to be determined. Other possibilities for SM acquisition by the bacteria are discussed [8]. Alternative routes for the transfer of SM and other lipids to the Chlamydia are discussed in an excellent recent review [6].