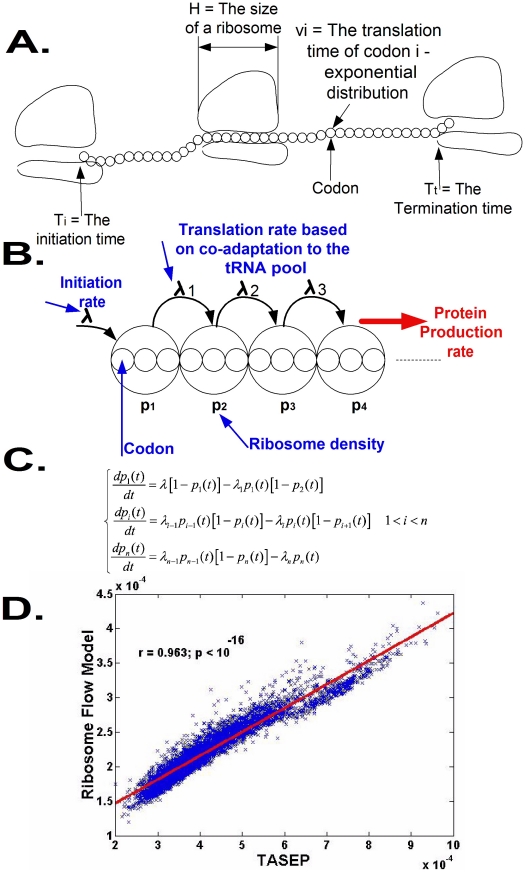
Figure 1. Basic properties of the Ribosome Flow Model (RFM).
A. The TASEP model: each codon has an exponentially distributed translation time; ribosomes have volume and can block each other. B. The RFM has two free parameters: the initiation rate λ and the number of codons C at each ‘site’ (proportional to the size of the ribosome). Each site has a corresponding transition rate 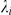 that is estimated based on the co-adaptation between the codons of the site and the tRNA pool of the organism (Methods). The output of the model consists of the steady state occupancy probabilities of ribosomes at each site and the steady state translation rates, or ribosome flow through the system. C. The set of differential equations that describe the RFM, denoted as equation (1). D. RFM vs. TASEP: the correlation between translation rates predicted by the two models is close to perfect (r = 0.963, p<10−16) while the running time of the TASEP is orders of magnitude longer (usually several days vs. minutes).
that is estimated based on the co-adaptation between the codons of the site and the tRNA pool of the organism (Methods). The output of the model consists of the steady state occupancy probabilities of ribosomes at each site and the steady state translation rates, or ribosome flow through the system. C. The set of differential equations that describe the RFM, denoted as equation (1). D. RFM vs. TASEP: the correlation between translation rates predicted by the two models is close to perfect (r = 0.963, p<10−16) while the running time of the TASEP is orders of magnitude longer (usually several days vs. minutes).