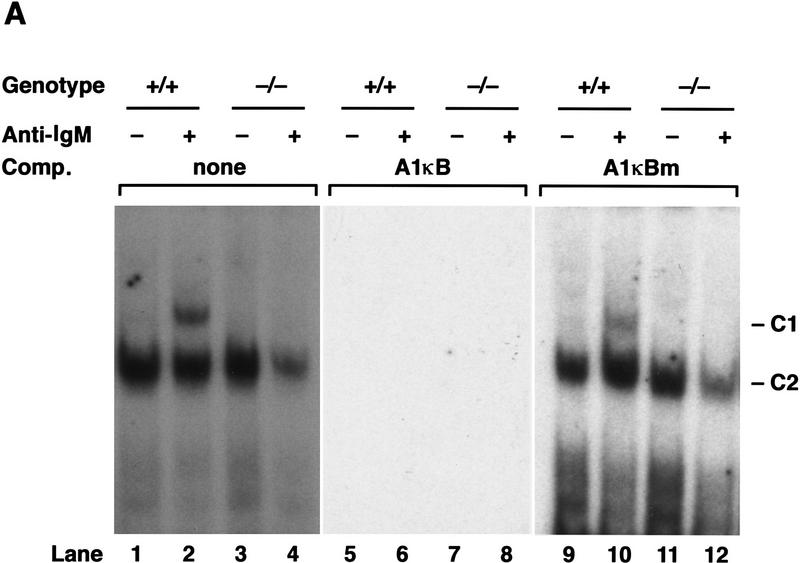
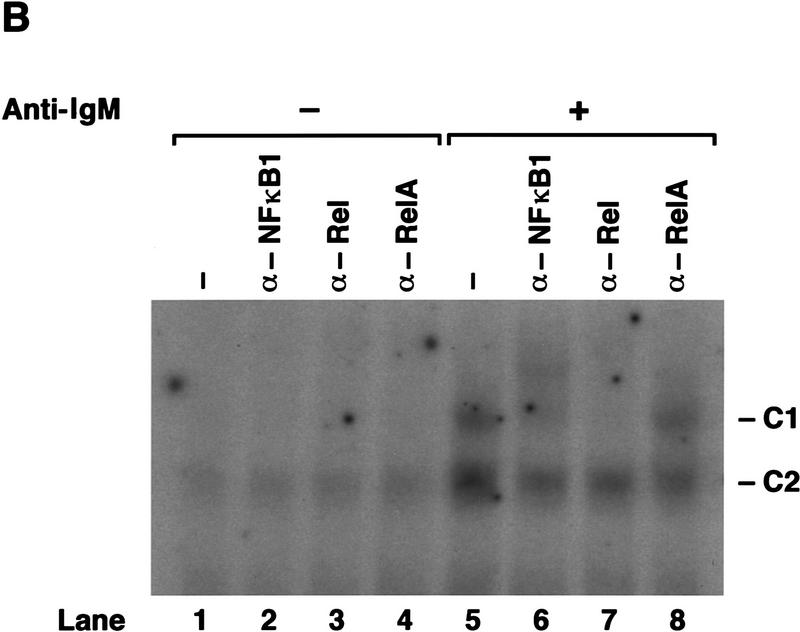
Figure 4.
Analysis of Rel/NF-κB complexes in resting and mitogen-stimulated B cells. Nuclear extracts (1–2 μg) isolated from purified normal and c-rel−/− splenic B cells stimulated with anti-IgM for 2 hr, then incubated with 32P-radiolabeled A1κB probe were resolved on 5% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels and exposed to autoradiography for 6–24 hr at −70°C. (A) A κB-binding complex rapidly induced by mitogen is absent in c-rel−/− B cells. Nuclear extracts from resting (lanes 1,3,5,7,9,11) and anti-IgM-stimulated (lanes 2,4,6,8,10,12) normal (lanes 1,2,5,6,9,10), and c-rel−/− (lanes 3,4,7,8,11,12) B cells were preincubated in the absence (lanes 1–4) or presence of a 50-fold molar excess of unlabeled A1κB (lanes 5–8) or A1κBm (lanes 9–12) probe before adding radiolabeled A1κB. The inducible slow mobility and constitutive fast mobility complexes are designated C1 and C2, respectively. (B) The inducible C1 complex is a Rel-containing heterodimer. Nuclear extracts from resting (lanes 1–4) and anti-IgM-stimulated (lanes 5–8) wild-type splenic B cells were incubated with preimmune (lanes 1,5) or NF-κB1 (lanes 2,6), Rel (lanes 3,7), and RelA (lanes 4,8) -specific sera before adding the radiolabeled A1κB probe.