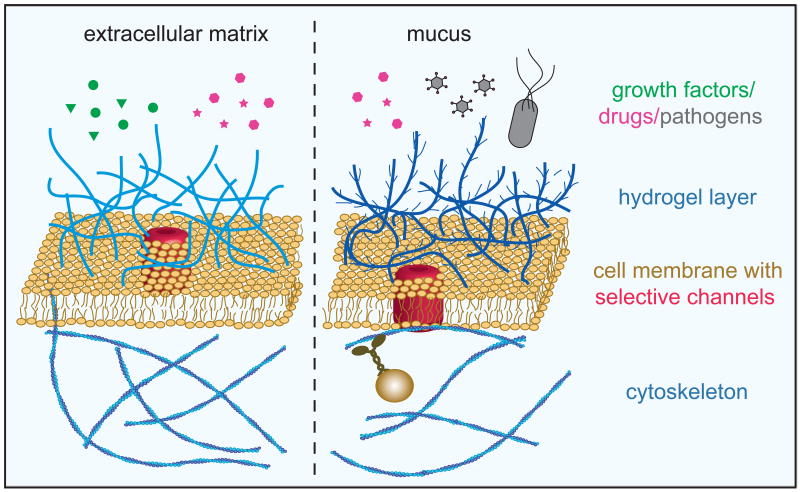
Figure 1.
The cell membrane/hydrogel barrier. Eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, which mediates both compartmentation and the exchange of material with the extracellular space. This plasma membrane is typically externally coated with a hydrogel such as the extracellular matrix or mucus, which provides an additional permeability barrier. For example, extracellular hydrogels can prevent molecules or microscopic particles such as viruses or bacteria from reaching the plasma membrane. The detailed microscopic mechanisms by which macromolecules or pathogens are retained by biological hydrogels are still poorly understood.