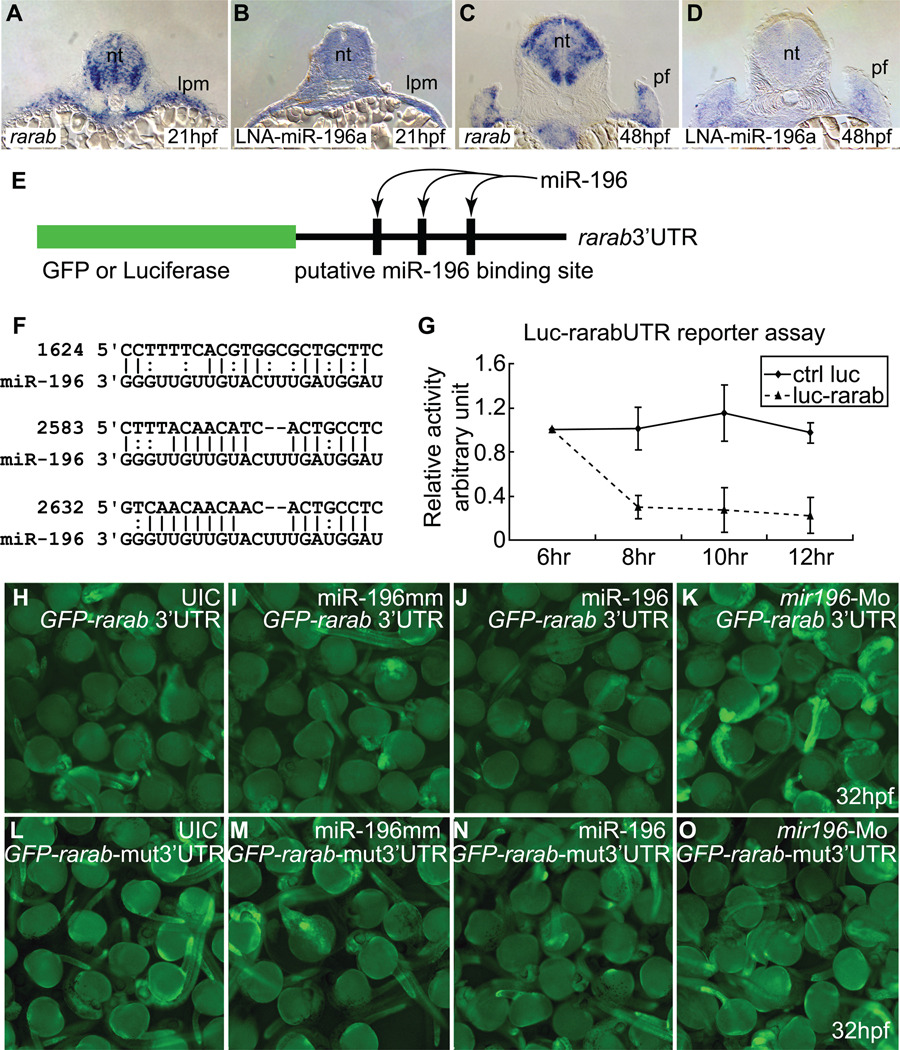
Figure 5.
rarab is a target of miR-196. (A–D) In situ hybridization on tissue sections for rarab (A, C) and miR-196 (using LNA probe, B, D) at 21 hpf (A, B) and 48 hpf (C, D) shows that rarab and miR-196 are co-expressed in the lateral plate mesoderm at 21 hpf (A, B) and medially in the pectoral fin bud at 48 hpf (C, D). (E–O) Reporter assays. (E) Reporter assay constructs used luciferase in (G) and GFP in (H–K). (F) The 3’UTR of rarab has three predicted binding sites for miR-196 (nucleotide position according to NM_131399, binding sites were retrieved or predicted from miRBase.com and MicroInspector). (G) miR-196 can interfere with expression of a luciferase reporter construct bearing the 3’UTR of rarab compared to control. This experiment was repeated three times. (H–K) GFP-rarab 3’UTR mRNA was injected into early cleavage stage embryos either by itself (H) or co-injected with miR-196 mismatch (I), with miR-196 duplex (J), or with mir196-Mo (K). miR-196 depressed fluorescence but mir196 knockdown enhanced fluorescence, as predicted by the hypothesis that miR-196 acts directly on the 3’UTR of rarab. This experiment was repeated four times. (L–O) The three predicted miR-196 binding sites were removed from the GFP-rarab 3’UTR construct to make a GFP-rarab-mut3’UTR. GFP-rarab mut3’UTR mRNA was injected into early cleavage stage embryos either by itself (L) or co-injected with miR-196 mismatch (M), with miR-196 duplex (N), or with mir196-Mo (O). miR-196 did not depress fluorescence (N) and mir196 knockdown did not enhance fluorescence (O) from this mutant construct. This experiment was repeated three times. lpm; lateral plate mesoderm; pf, pectoral fin bud.