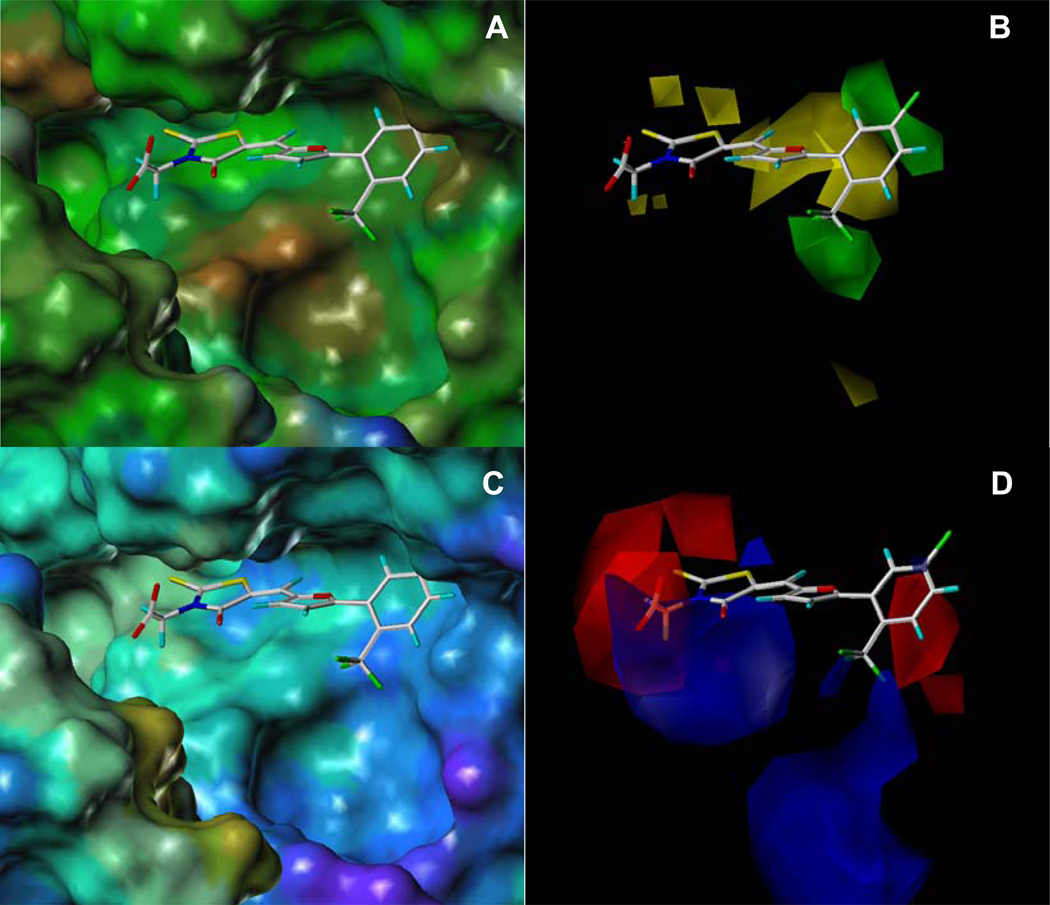
Figure 3.
Comparison of (A) hydrophobic and hydrophilic potential molecular surface (MOLCAD) 26 of the substrate binding site of LF in complex with compound 8 with (B) CoMFA contour plots of steric field contributions. Comparison of the (C) electrostatic potential molecular surfaces (MOLCAD) with (D) CoMFA contour plots of electrostatic field contributions. In (A), the hydrophobic and hydrophilic areas are displayed in brown and blue, respectively, while green surfaces represent an intermediate hydrophobicity. In (B), green contours indicate the regions where the addition of bulky groups may increase activity and yellow contours indicate the regions where the addition of bulky groups may decrease activity. In (C), positive and negative areas are displayed in red and blue, respectively, while cyan surfaces represent neutral areas. The color code follows the definitions of MOLCAD. 26 In (D), blue contours indicate regions where less electronegative groups may increase activity. Red contours indicate regions where more electronegative groups may increase activity.