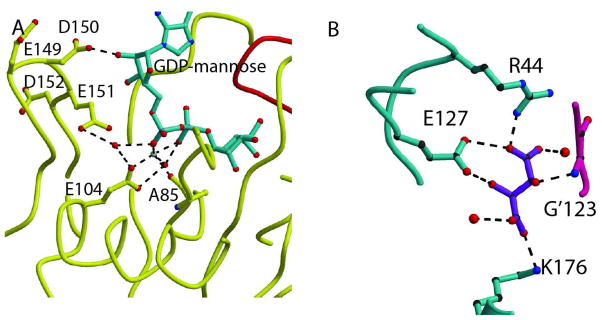
Fig. 4. Mechanistic insight.
A. GDPMK active site showing all residues and water molecules that are present near the diphosphate bond. E151 is in an ideal position to act as the catalytic base, but its mutation shows no large reduction of activity. B. Tartrate recognition in wild type structure. The bound tartrate is coordinated by hydrogen bonds to K176, R44, and E127 of one monomer and the amide NH of G’123 in the other monomer. All of these residues are involved in the mannose binding pocket.