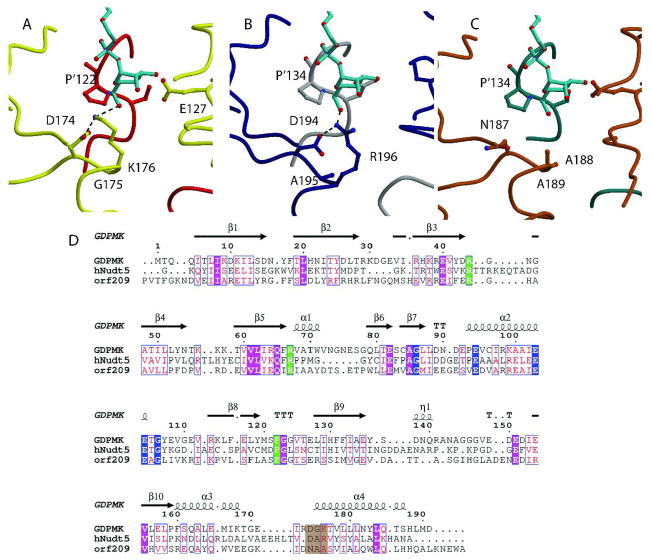
Fig. 6. Structural Alignment of GDPMK (CAQ32837.1), HsADPRase from H. sapiens (CAG33476.1), and EcADPRase from E. coli (NP_417506.1).
A. GDPMK is colored red and yellow. Two hydroxyl oxygens of the GDP-mannose make hydrogen bonds to E’127 and S’121 of the other monomer. These residues are conserved in the other two enzymes. B. HsADPRase is gray and darkblue; C. EcADPRase is colored dark cyan and brown. The main difference between the three enzymes is the presence of K176 in GDPMK, which is partly conserved as R196 in HsADPRase but not conserved in EcADPRase where it is an alanine (seen in brown). D. Sequences of the three enzymes. Nudix identities are colored blue, substrate recognition identities are in green, and residues in a brown background represent the putative mannose recognition site.