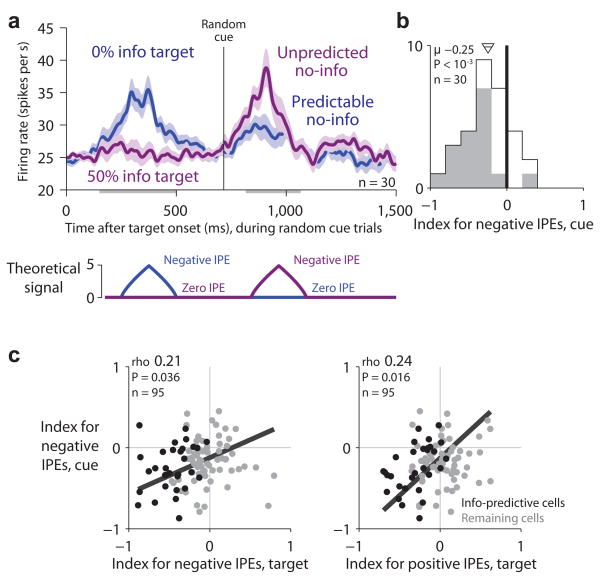
Figure 5.
Lateral habenula activity related to negative information prediction errors evoked by denial of reward information. (a) Average activity of information-predictive neurons on trials when random cues were presented (top) resembled the theoretical inverted IPE signal (bottom; model uses the same conventions as in Fig. 4). Activity is shown in response to the target array (left) and the onset of the random cues (right) for trials when the information probability was 0% (blue, ‘predictable no-info’) or 50% (purple, ‘unpredicted no-info’). Same format for smoothing and error regions as Fig. 2a. This population was excited by unpredicted no-info. (b) Single-neuron indexes for coding negative IPEs in response to the random cues. Same format as Fig. 3d,e, but showing the subpopulation of information-predictive neurons. (c) Neurons with strong negative IPE signals in response to the random cues tended to have strong negative IPE signals (left) and positive IPE signals (right) in response to the targets. Same format as Fig. 3f.