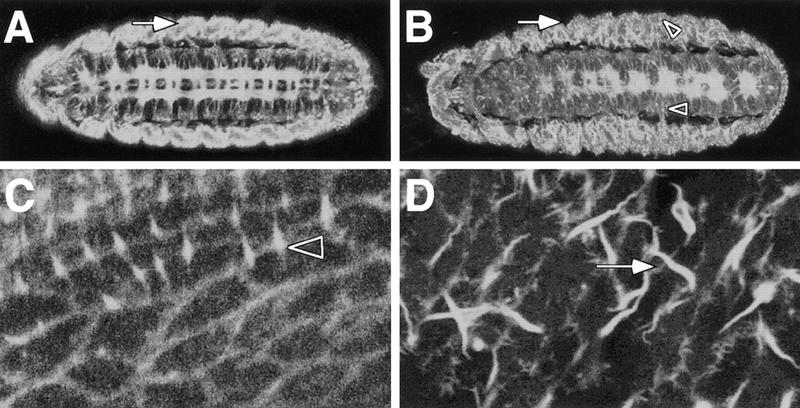
Figure 7.
kette affects the cytoskeleton. GFP–MOESIN was used to monitor the organization of the F-actin bundles. (A–D) Confocal images obtained from whole mount stage 16 embryos, anterior is to the left. (A) Distinct F-actin expression can be detected in the CNS axons, the ectoderm and the somatic musculature (arrow). (B) In mutant kette embryos, the CNS axon tracts are disorganized as seen in Fig. 1. The organization of F-actin fibers in the lateral body wall is abnormal. No clear concentration of staining can be found at the apical surface of the embryo. In addition, a granular appearance of F-actin staining can be observed in the nervous system as well as in the lateral body wall (arrowheads). (C) Tangential view of the dorsal epidermis. F-actin bundles line up the cell boundaries. Some cells project fine hairs (arrowhead). (D) Similar view of a kette mutant embryo. The cell borders are not staining as clear as in wild type. In addition, long hair-like structures are visible that are not found in the wild type (arrow).