Table 1.
Allylic alcohols 2a–2l via ruthenium catalyzed transfer hydrogenative coupling of butyne to alcohols 1a–1l.a
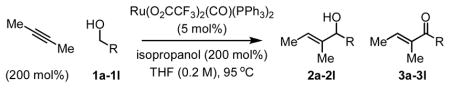 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Alcohol | Product | R | Time (h) | Yield 2 (3) |
| 1 | 1a | 2a (3a) | Ph | 9 | 72% (4%)b |
| 2 | 1b | 2b (3b) | p-NO2-Ph | 13 | 78% (12%) |
| 3 | 1c | 2c (3c) | p-Br-Ph | 13 | 81% (7%) |
| 4 | 1d | 2d (3d) | p-CO2Me-Ph | 13 | 81% (10%) |
| 5 | 1e | 2e (3e) | m-MeO-Ph | 13 | 78% (6%) |
| 6 | 1f | 2f (3f) | m-F-Ph | 13 | 79% (11%) |
| 7 | 1g | 2g (3g) | 3,5-Cl2-Ph | 13 | 76% (14%) |
| 8 | 1h | 2h (3h) | 3-Br, 4-F-Ph | 9 | 75% (< 1%) |
| 9 | 1i | 2i (3i) | (CH2)2OBn | 13 | 69% (< 1%) |
| 10 | 1j | 2j (3j) | (CH2)3OBn | 18 | 65% (< 1%) |
| 11 | 1k | 2k (3k) | (CH2)2NPhtl | 18 | 61% (< 1%) |
| 12 | 1l | 2l (3l) | CH2(o-Br-Ph) | 13 | 75% (< 1%)b |
Cited yields are of material isolated by silica gel chromatography and refer to pure 2a–2l free of any enone byproduct.
The reaction was conducted at 0.6 M concentration.
