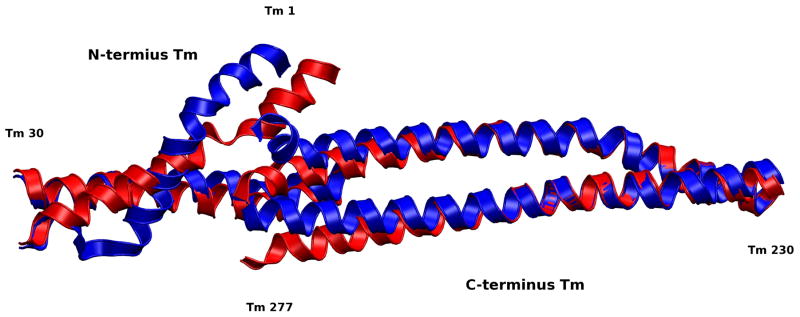
Figure 13.
Alignment of Ca2+-saturated and Ca2+-depleted average structures of overlapping Tm. The overlapping region of Tm is important for its affinity to actin and flexibility.(15) The significant changes we observe in this region appear despite the fact that both strands of Tm are constrained at each end by the remaining Tm in the closed position. The loss of secondary structure we observe in these average structures is likely the result of resistance to fluctuations by these constraints, an indicator that changes in this region could shift the equilibrium of more than just the overlap region. We expect that the loss of secondary structure would not occur if the remainder of Tm was allowed to move freely and that Tm would shift toward the closed state when our model is in the Ca2+-depleted state, and possibly toward the open state when our model is in the Ca2+-saturated state which would work in tandem with actomyosin interactions. In our model residues 245–277 of the C-terminus Tm and residues 1–30 of the N-terminus Tm are allowed to move freely, the remaining residues have their alpha carbons fixed in the closed position.