Fig. 2. Model for activation of RIG-I and MDA-5 by RNA.
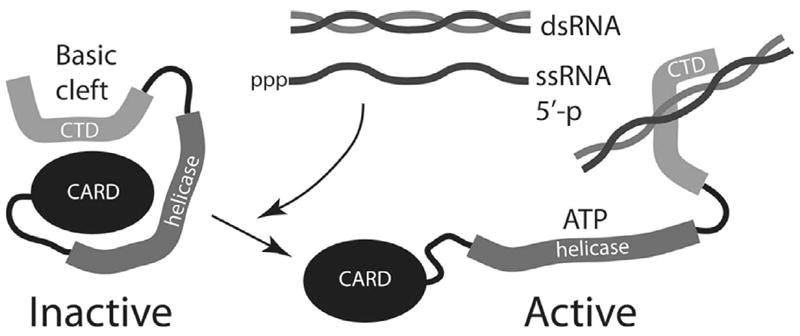
In the absence of RNA, the sensor molecule is folded in an inactive state, with the CARD domain occluded by the CTD. The latter also contains the binding sites for RNA. When RNAs are produced in virus-infected cells (either dsRNA or ssRNA with 5’-phosphates), these bind the CTD and cause a conformational change that exposes the CARD domain. ATP is required for the conformational change. The CARD domain then interacts with downstream signaling molecules, leading to IFN transcription.
