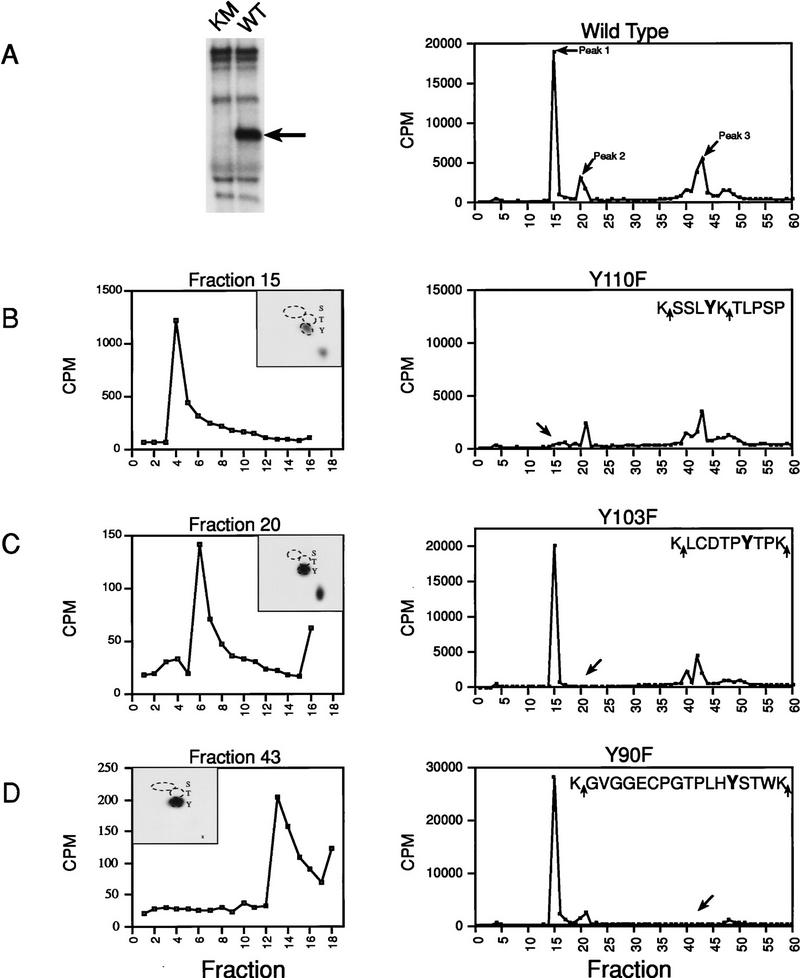
Figure 3.
Identification of Xe-Wee1 autophosphorylation sites. Wild type (WT) and kinase mutant (KM) Xe-Wee1 were translated in vitro and following immunoprecipitation, immune complex autokinase reactions were performed. After separation by SDS-PAGE (A, left), the wild-type 32P-labeled protein was eluted from the gel matrix, precipitated with TCA, and digested with either trypsin (which cleaves after Lys and Arg residues) or Lys-C (which cleaves after Lys residues). In the analysis of invitro-phosphorylated Xe-Wee1, both enzymes generated identical cleavage patterns, as the sites flanking the phosphopeptides were always lysine residues (B–D, right panels, sequences). The profile generated from the HPLC analysis of the wild-type Xe-Wee1 revealed three peaks of radioactivity (A, right). The peptides in fractions 15, 20, and 43, were subjected to phospho-amino acid analysis and two-dimensional thin-layer electrophoresis (B–D, left panels, insets), and Edman degradation (B–D, left panels). Each of the predicted tyrosine autophosphorylation sites was substituted with a phenylalanine residue, and the mutated versions of Xe-Wee1 were labeled with 32P in an autokinase assay and processed for HPLC analysis as described above; Y110F (B, right), Y103F (C, right), and Y90F (D, right). The amino acid sequence of the phosphopeptides is shown in the insets, arrows indicate LysC/trypsin cleavage sites.