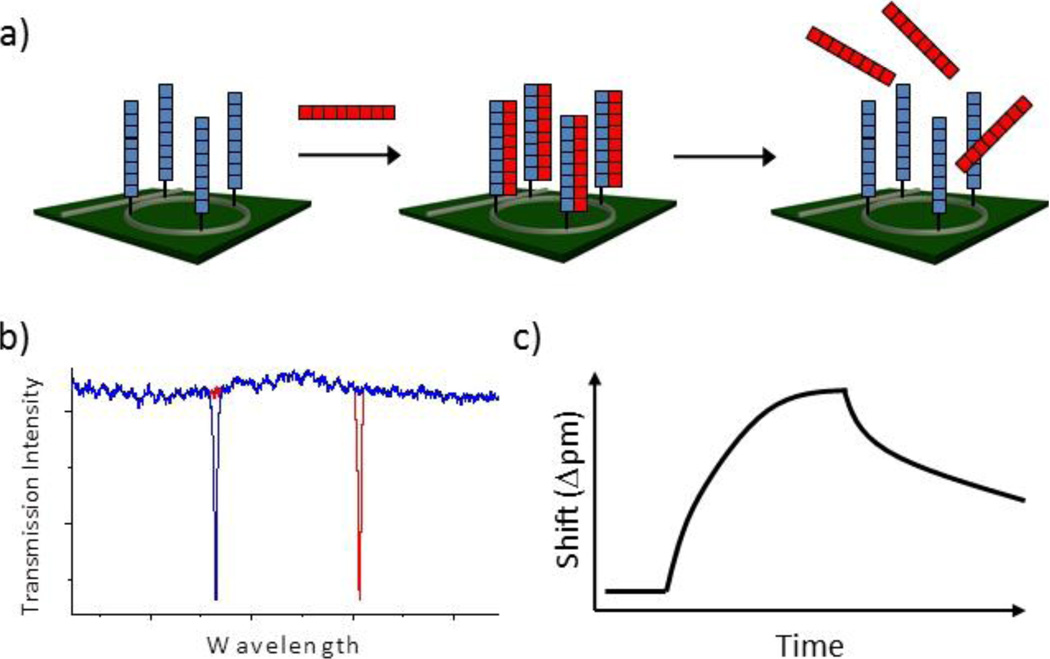
Scheme 1.
a) Microring resonators presenting single-stranded DNA capture probes can be used to detect the hybridization of complementary target probes and dissociation of the resulting duplex can be used to identify single nucleotide sequence mismatches. b) The wavelength of optical resonances supported by microrings is responsive to hybridization and duplex melting events. c) Shifts in resonance wavelength are measured in real-time, allowing access to binding and unbinding kinetics, which are used both for quantitation and SNP identification.