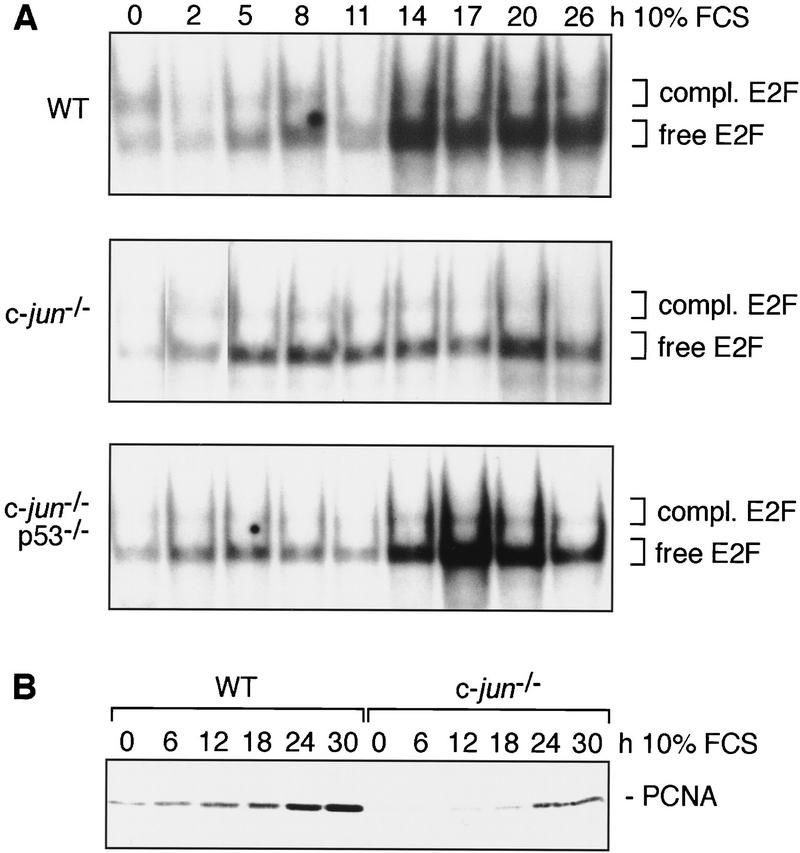
Figure 6.
Deletion of c-jun leads to poor activation of E2F, which can be rescued by simultaneous deletion of p53. (A) DNA-bound E2F complexes in synchronized wild-type (WT), c-jun−/−, and c-jun−/−p53−/− 3T3 fibroblasts were analyzed by electrophoretic mobility-shift assays (EMSA) using an oligonucleotide containing the consensus E2F-binding site. Whole-cell extracts were prepared at the indicated times after restimulation of quiescent cells. All complexes detected are specific as they were competed by an excess of unlabeled wild-type competitor but not by an oligonucleotide in which the E2F site was mutated (not shown). The amounts of extract used per lane were normalized by measuring protein concentrations and by quantitation of retarded bands formed with an SP-1 probe. The positions of free (active) E2F and of E2F complexed to pRb family proteins (compl. E2F) are indicated. (B) Western blot analysis of the E2F target gene PCNA in G0 synchronized wild-type and c-jun−/− 3T3 fibroblasts after serum stimulation for the indicated times.